Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
II PUC CHEMISTRY (P.U. BOARD LATEST MODEL QUESTION PAPER - 3)
SUNSTAR PUBLICATION|Exercise PART - C|16 VideosII PUC CHEMISTRY (P.U. BOARD LATEST MODEL QUESTION PAPER - 2)
SUNSTAR PUBLICATION|Exercise PART - D|28 VideosII PUC CHEMISTRY (SUPPLEMENTARY EXAM QUESTION PAPER JULY - 2014)
SUNSTAR PUBLICATION|Exercise PART - D|22 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUNSTAR PUBLICATION-II PUC CHEMISTRY (P.U. BOARD LATEST MODEL QUESTION PAPER - 3)-PART - D
- c) Resistance of a conductivity cell containing 0.1 M KCl solution is ...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for half life period of a first order reaction.
Text Solution
|
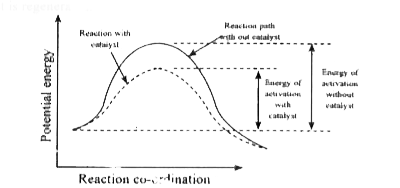
- Explain the influence of a catalyst on rate of reaction.
Text Solution
|
- c) For the reaction, H(2)+I(2)rarr 2HI, the rate of disappearance of H...
Text Solution
|
- What is Brownain movement ? What is the cause for it ?
Text Solution
|
- Write the difference between physisorption and chemisorption with resp...
Text Solution
|
- Name the enzyme that catalyses the reaction: H(2)NCONH(2)+H(2)Orarr2NH...
Text Solution
|
- a) Write S(N)1 mechanism for the hydrolysis of 2-Bromo-2-methyl propan...
Text Solution
|
- In the preparation of aryl halides by Sandmeyer's reaction, name the i...
Text Solution
|
- Write the chemical equation for the conversion of, i) phenol to sali...
Text Solution
|
- Explain Williamson's ether synthesis.
Text Solution
|
- Which class of alcohols do not readily form turbidity with Lucas reage...
Text Solution
|
- Explain Clemmensen reduction with an example.
Text Solution
|
- Name the reaction to obtain benzaldehyde from: i) toluene ii) benzen...
Text Solution
|
- How are primary amines prepared from nitro compounds? Write the equati...
Text Solution
|
- How does Hinsberg's reagent react with ethyl amine? Write the equation...
Text Solution
|
- Write the IUPAC name of
Text Solution
|
- a) Name the water insoluble component of starch.
Text Solution
|
- Name the type of linkage between two nucleotides in nucleic acid.
Text Solution
|
- With respect to proteins, what do you mean by i) primary structure i...
Text Solution
|