Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
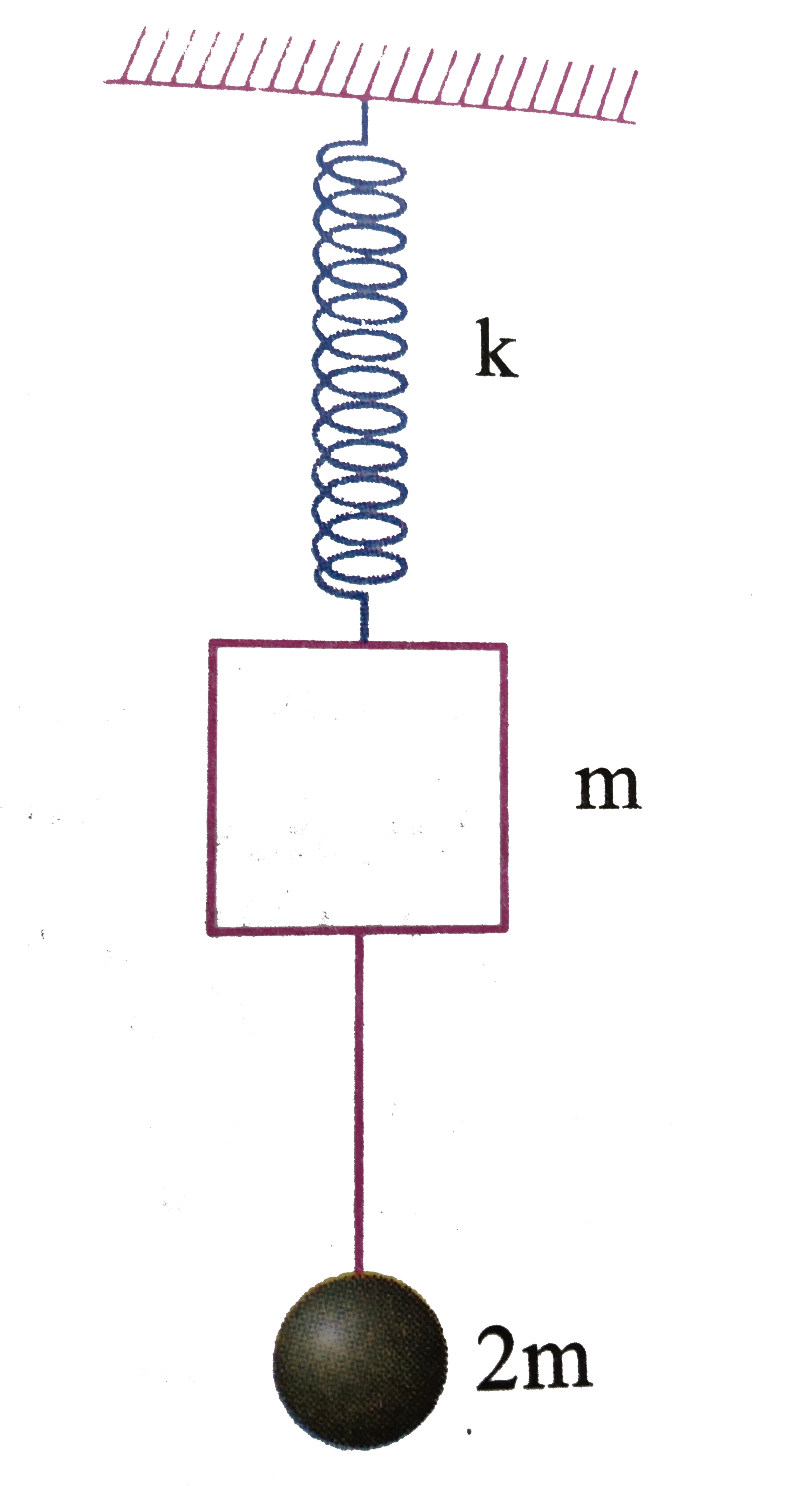
- A bob of mass 2m hanges by a string attached to the block of mass m of...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in Fig there is no friction between of mass 2...
Text Solution
|
- A bob of mass 2m hanges by a string attached to the block of mass m of...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum bob has a mass ''m'' and length ''L'' . The bob is d...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2m is attached to a string of length L = 5 m. The bloc...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown the spring is compressed by 'x(0)' and released . ...
Text Solution
|
- In the fig shown, a block of mass M is attached to the spring and anot...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in figure , there is friction between the bl...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in figure, there is a friction force between ...
Text Solution
|