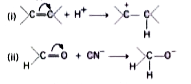Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
ICSE|Exercise ESSAY ( LONG ANSWER ) TYPE QUESTIONS|42 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
ICSE|Exercise OBJECTIVE ( MULTIPLE CHOICE ) TYPE QUESTIONS|142 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
ICSE|Exercise VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|87 VideosHYDROGEN
ICSE|Exercise NCERT TEXT-BOOK EXERCISE (With Hints and Solutions)|53 VideosREDOX REACTIONS (OXIDATION AND REDUCTION)
ICSE|Exercise NCERT TEXT-BOOK. EXERCISES ((With Hints and Solutions)|69 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ICSE-ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES -SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
- Why is dichloroacetic acid stronger than monochloroacetic acid ?
Text Solution
|
- Define electromeric effect.
Text Solution
|
- What type of effects are involved in the following reactions ?
Text Solution
|
- What are the main points of difference between inductive and electrome...
Text Solution
|
- When does mesomeric effect come into existence ? Illustrate with examp...
Text Solution
|
- Define mesomeric effect and differentiate + M-effect from - M-effect.
Text Solution
|
- Compare inductive effect with mesomeric effect.
Text Solution
|
- What do you understand by hyperconjugation effect ? Illustrate with an...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the Hyperconjugation effect is also termed as 'no bond reso...
Text Solution
|
- Why is the hyperconjugation effect exerted by a methyl group greater t...
Text Solution
|
- Define heterolytic fission of a covalent bond.
Text Solution
|
- Why is a 3^@ radical more stable as compared to 1^@ and 2^@ free r...
Text Solution
|
- What are carbocations ? Give two examples.
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the orbital structure of a carbocation.
Text Solution
|
- What is relative order of reactivity of various types of carbocations ...
Text Solution
|
- Define carbanion and discuss its orbital structure.
Text Solution
|
- Why is 1^@ carbanion more stable than a 2 carbanion ?
Text Solution
|
- What are carbenes ?
Text Solution
|
- What are electrophilic reagents ? Give at least three examples.
Text Solution
|
- Why do free radicals and carbenes act as electrophiles ?
Text Solution
|