Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ICSE-SPECTRUM-TYPE 3 DIAGRAM BASED MCQ:
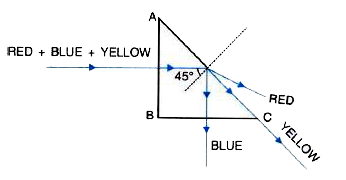
- A beam consisting of red, blue and yellow colours is incident normally...
Text Solution
|
- Name the radiations used while taking the following photograph:
Text Solution
|
- Name the waves given out by the two-dish shown in the figure:
Text Solution
|
- The device used in the figure uses radiations to cook food.
Text Solution
|
- A skeletal analysis of skull is shown in the figure below. Name the ra...
Text Solution
|
- Name the machine shown in the figure using gamma radiations in detecti...
Text Solution
|