Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
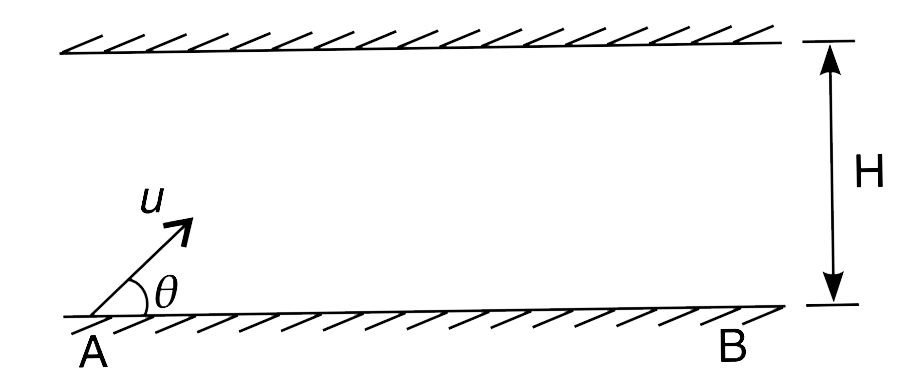
- A ball is projected from the floor of a long hall having a roof height...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected vertically down with an initial velocity from a he...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is shot in a long hall having a roof at a height of 10m with 25...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected from the floor of a long hall having a roof height...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is shot in a long hall having a roof at a height of 15 cm with ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is kicked at an angle of 30^(@) with the vertical. If the horiz...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected horizontally from a tower with a velocity of 4 ms^...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected vertically down with an initial velocity from a he...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected with initial speed u at an angle theta above the h...
Text Solution
|