Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
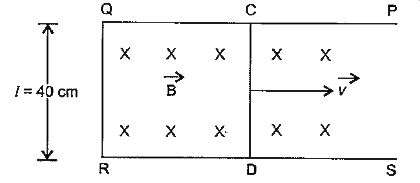
- A metallic rod CD rests on a thick metallic wire PQRS with arms PQ and...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of length l is hinged at the point M and is rotating ab...
Text Solution
|
- A wire is bent in the form of a V shape and placed in a horizontal pl...
Text Solution
|
- PQ is a uniform rod of length l and mass m carrying current i and is s...
Text Solution
|
- Two thick rods AB, CD are placed parallel to each other at a distance ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod PQ is connected to the capacitor plates. The rod is placed in a ...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel fixed conducting rails are l distance apart. They are con...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic V shaped rod OAC is rotated with respect to one of its end ...
Text Solution
|
- Two long parallel metallic wires with a resistance 'R' from a horizont...
Text Solution
|