A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A short electric dipole (which consists of two point charges, + q and ...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q is placed at the centre of a cube of side l what is the el...
Text Solution
|
- एक घन के अन्दर आठ विद्युत् द्विध्रुव, जिनमें प्रत्येक के आवेश का परिमा...
Text Solution
|
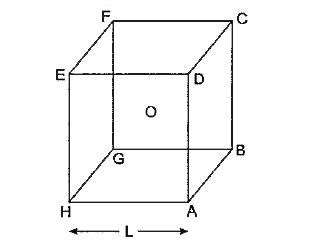
- A charged particle q is placed at the centre O of a cube of lenngth L ...
Text Solution
|
- An electric charge q is placed at the centre of a cube of side l. The ...
Text Solution
|
- एक बिन्दु आवेश + q, L भुजा वाले घन के मध्य-बिन्दु पर रखा है, घन से निक...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge q is placed at the centre of a cube of side length L . ...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q is placed at the centre of a cube of side l what is the ele...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge +q is placed at the centre of a cube of side L. The ele...
Text Solution
|