Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
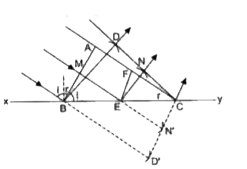
- Define the term wavefront. Using Huygens' wave theory, verify the laws...
Text Solution
|
- When light passes from a denser medium to a rarer medium
Text Solution
|
- Huygens wave theory is used
Text Solution
|
- Define a wavefront. Using Huygens' principle verify the laws of reflec...
Text Solution
|
- Define a wavefront . Using Huygens principle ,verify the laws of refle...
Text Solution
|
- Using Huygens' principle for the wave theory of light, verify the law ...
Text Solution
|
- Prove laws of reflection using Huygens' principal. (OR) Proof for laws...
Text Solution
|
- State Huygens' principle and prove the laws of reflection on the basis...
Text Solution
|
- Define a wavefront. Use huygen's principle to verify the laws of defra...
Text Solution
|