Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
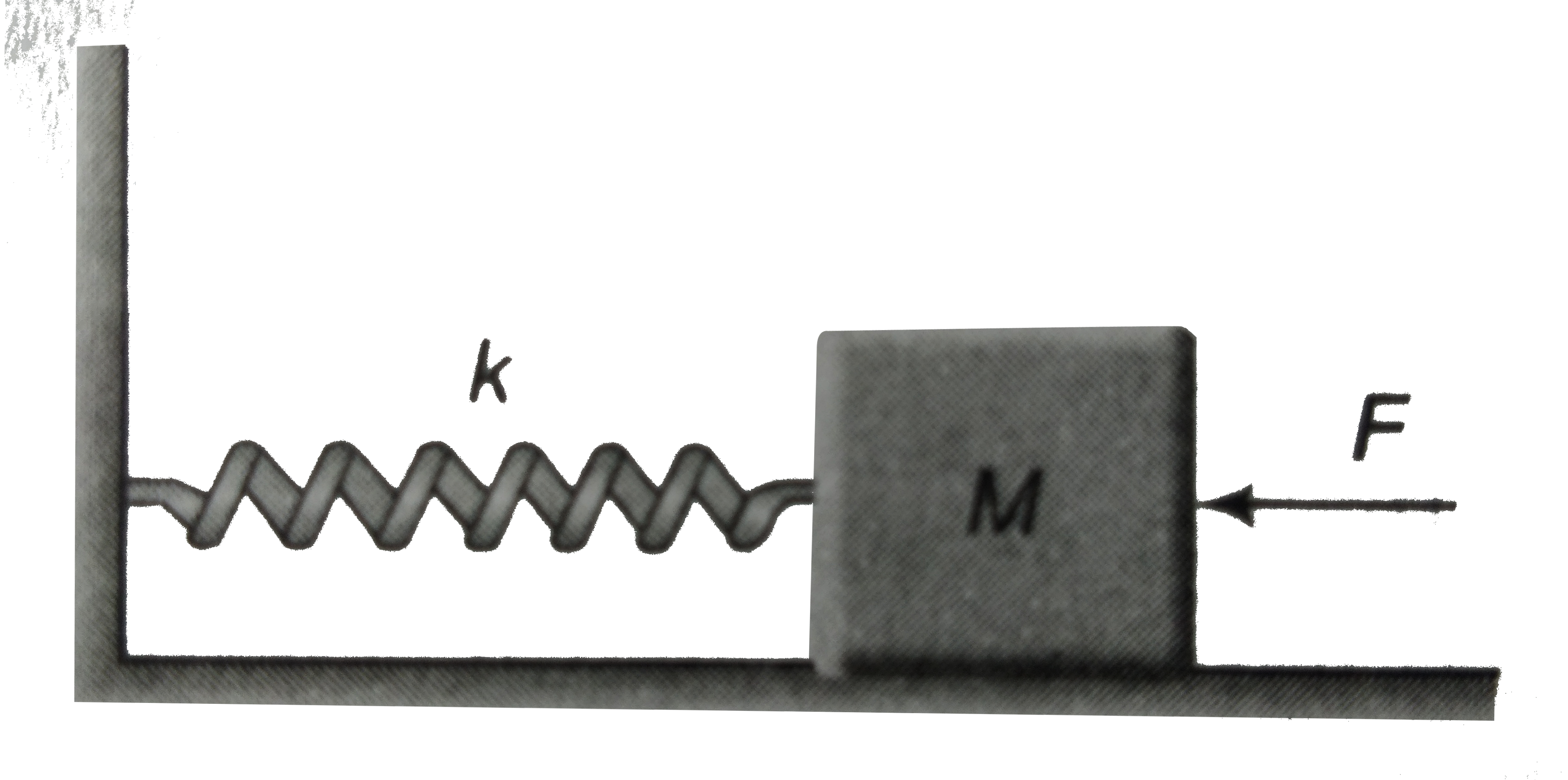
- In figure, k = 100 N//m, M = 1kg and F = 10 N (a) Find the compre...
Text Solution
|
- Each of the blocks shown in figure has mass 1 kg. The rear block moves...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2.0 kg is moving on a frictionless horizontal surface ...
Text Solution
|
- In figue k=100Nm^-1 M=1kg and F=10N. a. Find the compression of the sp...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows, a 3.5 kg block accelerated by a compressed spring whose ...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, k = 100 N//m, M = 1kg and F = 10 N (a) Find the compression...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m moving at a speed v0 compresses a spring of spring c...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 200 g is given velocity 2(m)//(s) on a horizontal surf...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, a block A of mass 2kg is moving to the right with a speed 5...
Text Solution
|