Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
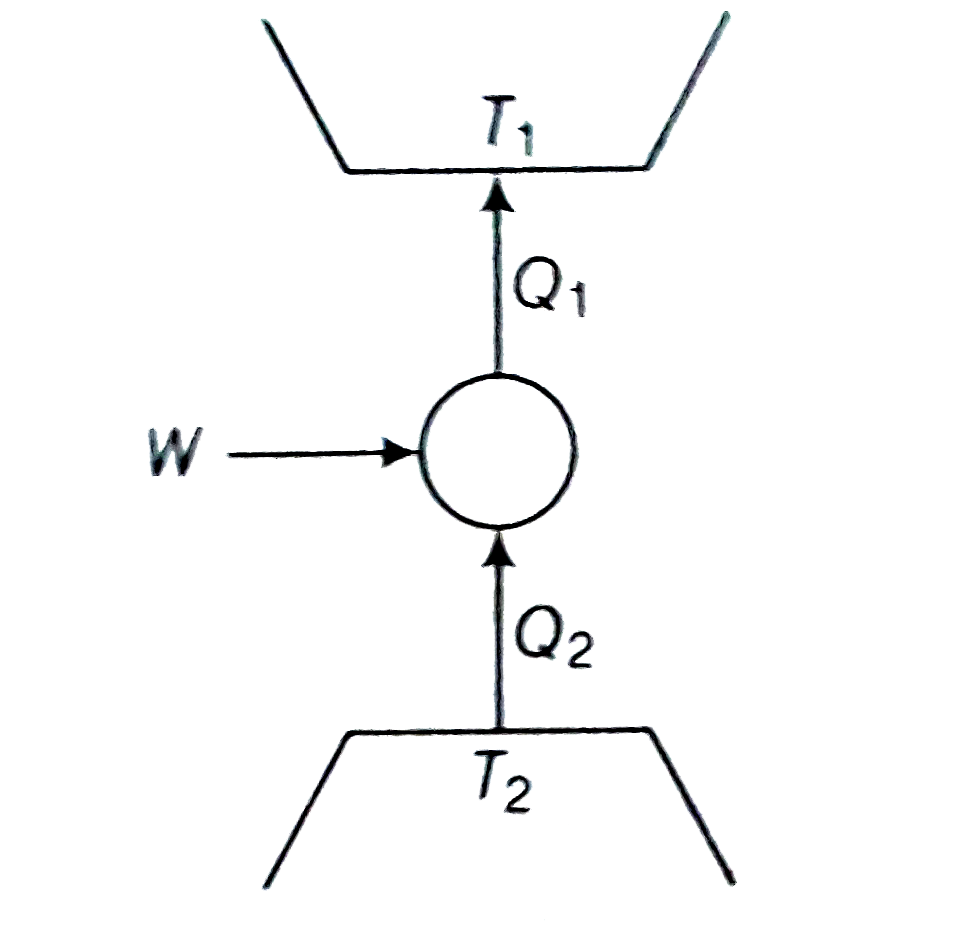
- Consider a heat engine as shown in figure. Q(1)and Q(2) are heat added...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a heat engine as shown in (figure). Q(1) and Q(2) are heat ad...
Text Solution
|
- A heat engine absorbs heat Q(1) at temperature T(1) and Q(2) at temper...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a heat engine as shown in figure. Q(1)and Q(2) are heat added...
Text Solution
|
- The efficiency of a heat engine is defined as the ratio of the mechani...
Text Solution
|
- The efficiency of a heat engine is defined as the ratio of the mechani...
Text Solution
|
- A heat engine absorbs heat Q(1) at temperature T(1) and heat Q(2) at t...
Text Solution
|
- A heat engine absorbs heat Q(1) at temperature T(1) and heat Q(2) at t...
Text Solution
|
- A heat engine absorbs heat q(1) from a source at temperature T(1) and ...
Text Solution
|