Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ICSE-SAMPLE PAPER 2015-SECTION-II
- A person standing between two vertical cliffs and 480 m from the neare...
Text Solution
|
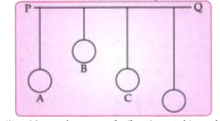
- In the diagram below, A, B, C, D are four pendulums suspended from the...
Text Solution
|
- In the diagram below, A, B, C, D are four pendulums suspended from the...
Text Solution
|
- In the diagram below, A, B, C, D are four pendulums suspended from the...
Text Solution
|
- Name the device used to increase the voltage at a generating station.
Text Solution
|
- At what frequency is A.C. supplied to residential houses ?
Text Solution
|
- Name the wire in a household electrical circuit to which the switch is...
Text Solution
|
- The relationship between the potential difference and the current in a...
Text Solution
|
- The relationship between the potential difference and the current in a...
Text Solution
|
- The relationship between the potential difference and the current in a...
Text Solution
|
- A cell of emf 2 V and internal resistance 1.2Omega is connected with a...
Text Solution
|
- A cell of emf 2 V and internal resistance 1.2Omega is connected with a...
Text Solution
|
- Name a gas caused by the Greenhouse effect.
Text Solution
|
- Which property of water makes it an effective coolant ?
Text Solution
|
- Water in lakes and ponds do not freeze at once in cold countries. Give...
Text Solution
|
- What is the principle of Calorimetry?
Text Solution
|
- Name the law on which this principle is based.
Text Solution
|
- State the effect of an increase of impurities on the melting point of ...
Text Solution
|
- A refrigerator converts 100 g of water at 20^(@)C to ice at -10^(@)C i...
Text Solution
|
- Thermionic emissions are related to
Text Solution
|