A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KVPY PREVIOUS YEAR-MOCK TEST 5-EXERCISE
- One quarter sector is cut from a uniform circular disc of radius R. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A gaseous mixture enclosed in a vessel consists of one gram mole of a ...
Text Solution
|
- v31
Text Solution
|
- A parallel plate capacitor C with plates of unit area and separation d...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel of volume V is evacuated by means of a piston air pump. One ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting loop is being pulled with speed v from region I of magnet...
Text Solution
|
- The current transfer ratio beta of a transistor is 50. The input resis...
Text Solution
|
- A metre long narrow bore held horizontally (and close at one end) cont...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniformring of radius R carrying uniform charge Q and mass M ro...
Text Solution
|
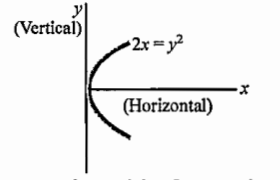
- The reflecting surface is represented by the equation 2x =y^2 as shown...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy of a particle of mass m is given by U(x){{:(E(0),...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder rolls up an inclined plane, reaches some height, and then r...
Text Solution
|
- The escape velocity of a body on the Earth’s surface isve. A body is t...
Text Solution
|
- A 10 kW drilling machine is used to drill a bore in a small aluminium ...
Text Solution
|
- A strip of wood of length l is placed on a smooth horizontal surface. ...
Text Solution
|
- A wind - powered generator convets and energy into electrical energy ...
Text Solution
|
- An object with uniform density ρ is attached to a spring that is known...
Text Solution
|
- A tiny spherical oil drop carrying a net charge q is balanced in still...
Text Solution
|
- The flow of blood in a large artery of an anaeshetized dog is diverted...
Text Solution
|