A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KVPY PREVIOUS YEAR-MOCK TEST 8-EXERCISE
- A ray of light is incident on a surface of glass slab at an angle 45^@...
Text Solution
|
- A charge Q is uniformly distributed over a long rod AB of length L as ...
Text Solution
|
- The graph of an object’s motion (along the x-axis) is shown in the fig...
Text Solution
|
- In an ideal YDSE when a glass plate (mu=1.5) of thickness t is introdu...
Text Solution
|
- Potential of certain points in circuit are maintained as marked. What ...
Text Solution
|
- If the wavelength of the first line of the Balmer series of hydrogen i...
Text Solution
|
- A bulb made of tungsten filament of surfece area 0.5 cm^2 is heated to...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical small ball of density rho is gently released in a liquid o...
Text Solution
|
- The rear side of a truck is open and a box of 40 kg mass is placed 5 m...
Text Solution
|
- N atoms of a radioactive element emit n alpha particles per second. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal rod of mass m and length L is pivoted at one end The rod'...
Text Solution
|
- Two simple pendulum of length 1m and 16m respectively are both given s...
Text Solution
|
- Water is filled up to a height h in a beaker of radiys R as shown in t...
Text Solution
|
- A police van moving on a highway with a speed of 30 km h^-1 fires a bu...
Text Solution
|
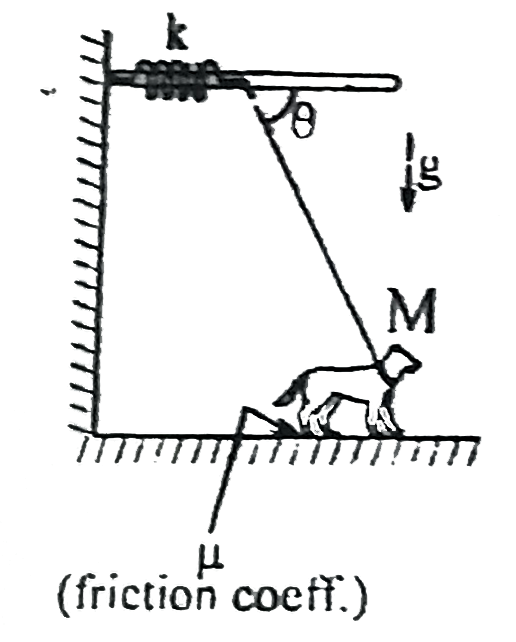
- A dog with mass M has its string attached to one end of a spring which...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical ladders, each of mass M and length L are resting on the ...
Text Solution
|
- Currents flowing in each of the circuits A and B respectively are
Text Solution
|
- The densitis of two solid spheres A and B of the same radii R very wit...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjacent diagram, CP represents a wavefront and AO & BP, the co...
Text Solution
|
- Two solid cylinders P and Q of same mass and same radius start rolling...
Text Solution
|