A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KVPY PREVIOUS YEAR-SOLVED PAPER 2018-EXAMPLE
- The complex that can exhibit linkage isomerism is
Text Solution
|
- The tendency of X in BX(3)(X=F,Cl,Ome, Nme) to form a pi bond with bor...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following statement about Langmuir isotherm : (i) The f...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following , the plot that correctly represents the conductom...
Text Solution
|
- The correct representation of wavelength intensity relationship of an ...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure (P)- volume (V)isotherm of a van der Waals gas, at the te...
Text Solution
|
- Give examples of two buffer solutions prepared by mixing two salt solu...
Text Solution
|
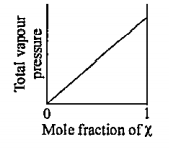
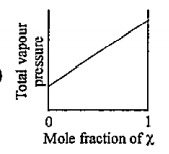
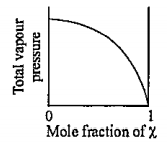
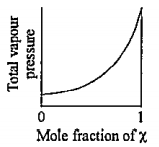
- The plot of total vapour pressure as a function of mole fraction of th...
Text Solution
|
- On complete hydrogenation, natural rubber produces
Text Solution
|
- The average energy of each hydrogen bond in A-T pair is x kcal mol^(-1...
Text Solution
|
- For the electrochemical cell shown below Pt|H2(p=1atm)|H^+(aq.,xM)||Cu...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reversible first - order reaction of X at an in...
Text Solution
|
- Nitroglycerine (MW =227.1) detonates according to the following equat...
Text Solution
|
- The heating of (NH(4))2Cr(2)O(7) produces another chromium compound al...
Text Solution
|
- The complex having the highest spin-only magnetic moment is
Text Solution
|
- Among Ce(4f^(1)5d^(1)6s^(2)), Nd(4f^(4)6s^(2)),Eu(4f^(7)6s^(2))" and "...
Text Solution
|
- The major product of the following reaction sequence,
Text Solution
|
- Among the following reactions ,a mixture of diastereomers is produced ...
Text Solution
|
- Reaction of phenol with NaOH followed by heating with CO(2) under high...
Text Solution
|
- Tetrapeptide is made of naturally occuring alanine , serine glycine an...
Text Solution
|