Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
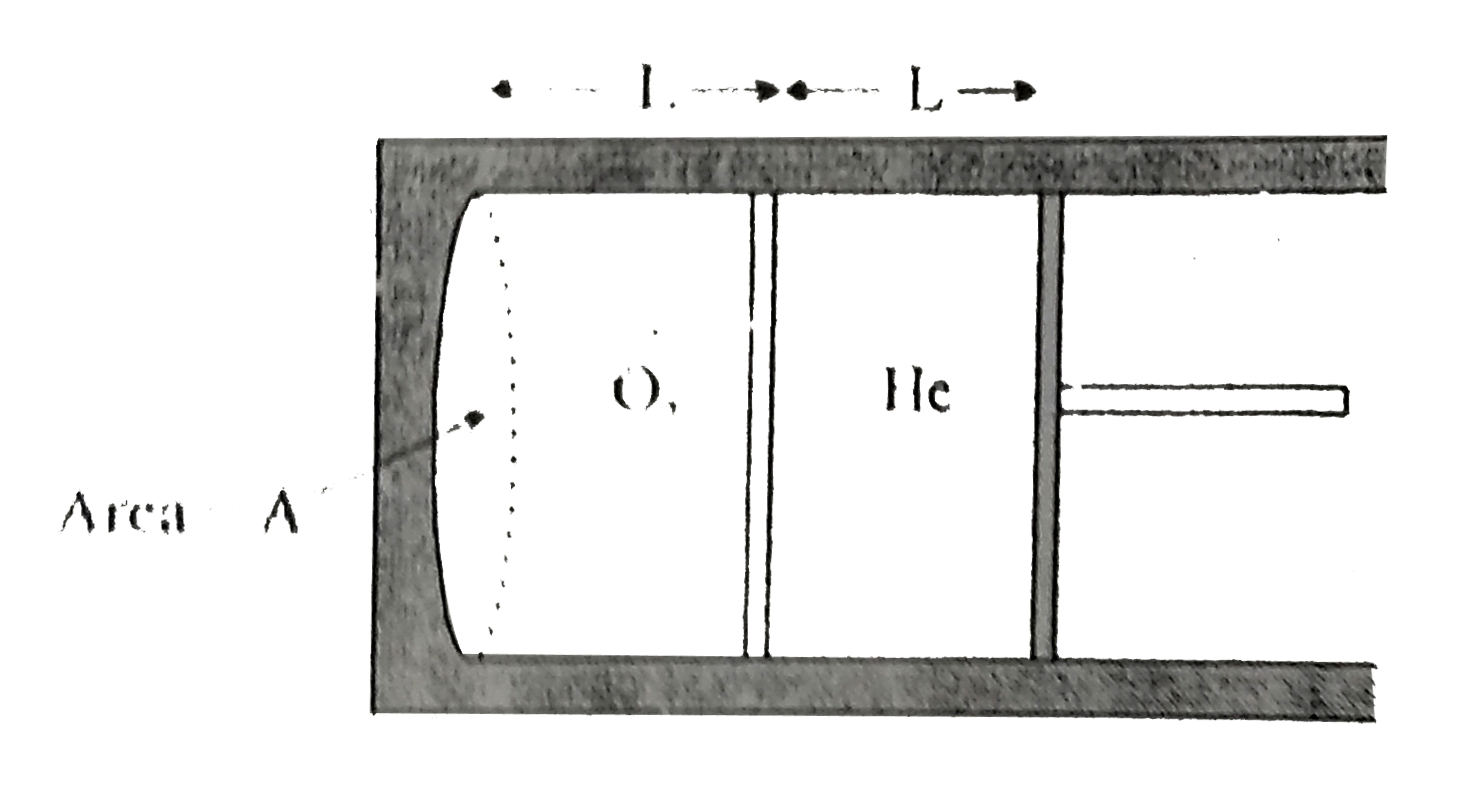
- An insulating cylinder contains equal volumes of He and O(2) separated...
Text Solution
|
- An insulating cylinder contains equal volumes of He and O(2) separated...
Text Solution
|
- A gas (lambda=1.3) is enclosed in an insulated vessel fitted with ins...
Text Solution
|
- गतिशील पिस्टन लगे सिलिंडर में मानक ताप व दाब पर 3 मोल हाइड्रोजन भरी है...
Text Solution
|
- गतिशील पिस्टन लगे किसी सिलिंडर में मानक ताप व दाब पर 3 मोल हाइड्रोजन भ...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder with a movable piston contains 3 moles of hydrogen at const...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder with a movable piston contains 3 moles of hydrogen at stand...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder with a movable piston contains 3 moles of hydrogen at stand...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder with a movable piston contains 3 moles of hydrogen at stand...
Text Solution
|