Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
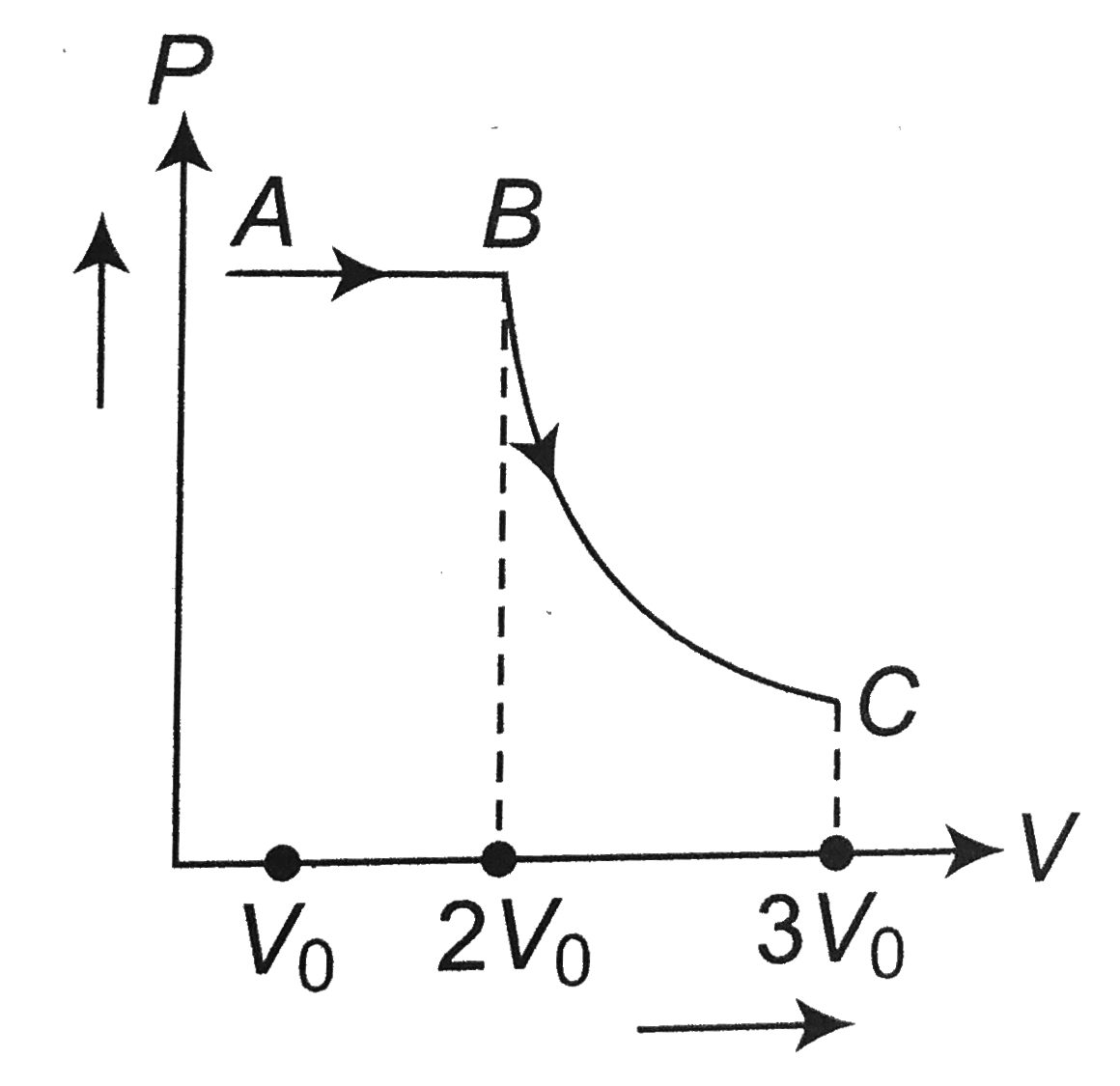
- One mole of a gas is subjected to two process AB and BC, one after the...
Text Solution
|
- Temperature of two moles of an ideal gas is increased by 300K in a pro...
Text Solution
|
- The cyclic process for 1 mole of an ideal gas is shown in the V-T diag...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas has an interal energy given by U=U(0)+2PV , w...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a gas is subjected to two process AB and BC, one after the...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas at initial temperature T, undergoes a quasi-s...
Text Solution
|
- Figure demonstrates a polytropic process (i.e.PV^(n) = constant ) for ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of ideal gas goes through a process pV^3 = Constant , where...
Text Solution
|
- एक आदर्श गैस के लिए एक उत्क्रमणीय चक्रीय नीचे आकृति में दिखाया गया है।...
Text Solution
|