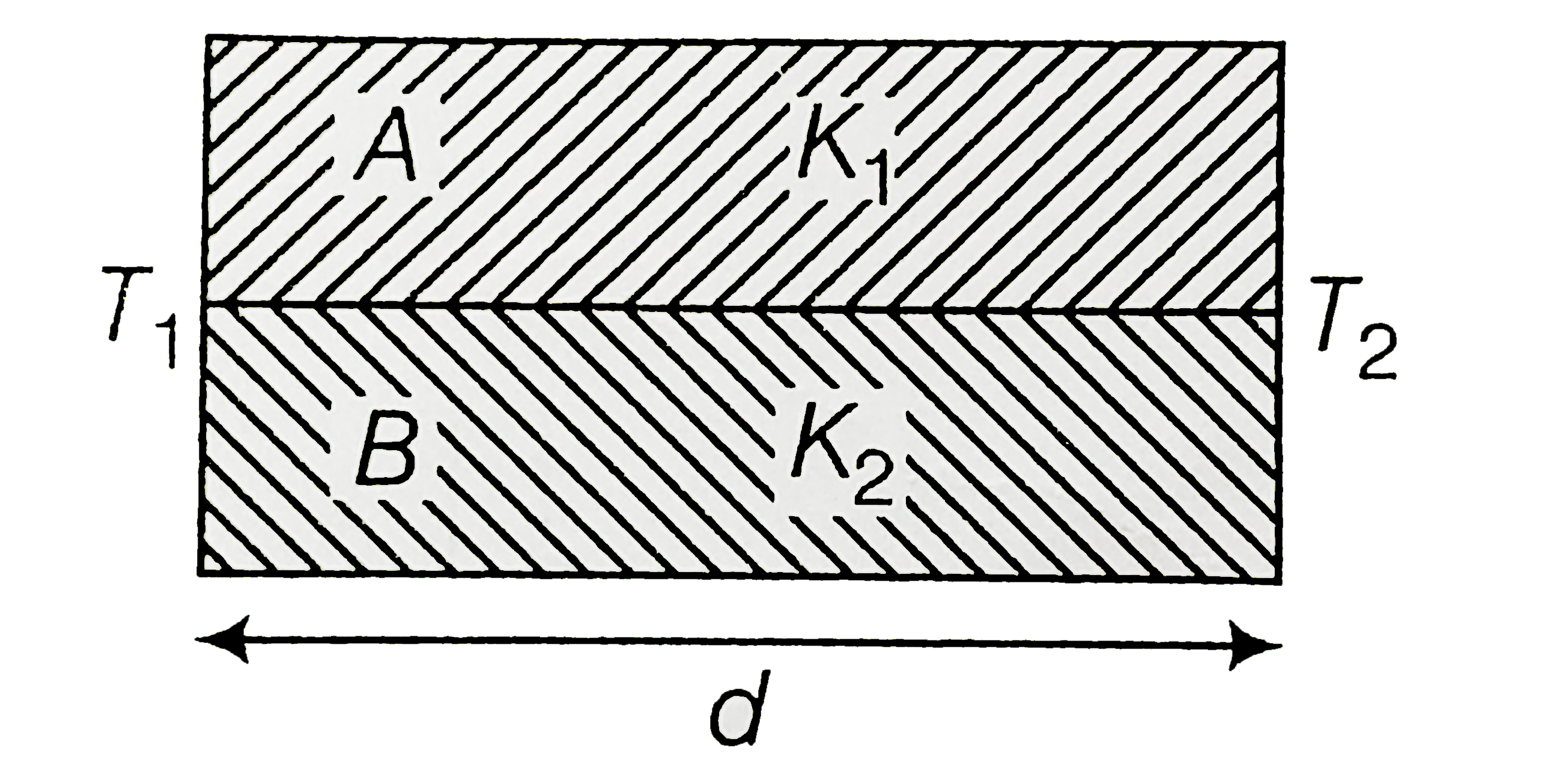
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two rods A and B of different materials are welded together as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods A and B of different materials are welded together as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods A and B of different materials are welded together as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods one is semi circular of thermal conductivity K(1) and otheir ...
Text Solution
|
- A slab consists of two layers of different materials of the same thick...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods of the same length and diameter, having thermal conductivitie...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical rods are made of different materials whose thermal condu...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods of same dimensions are arranged as shown in the figure. The...
Text Solution
|
- Five rods of same dimensions are arranged as shown in the figure. They...
Text Solution
|