Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ICSE-MATHEMATICS-2019-SECTION-B
- Given [(4,2),(-1,1)]M = 6 I, where M is a matrix and I is the unit mat...
Text Solution
|
- Given [(4,2),(-1,1)]M = 6 I, where M is a matrix and I is the unit mat...
Text Solution
|
- The sum of the first three terms of an Arithmeic Progression (A.P.) is...
Text Solution
|
- The vertices of a DeltaABC are A (3, 8), B (-1, 2) and C (6, -6). Find...
Text Solution
|
- The vertices of a DeltaABC are A(3, 8), B(-1, 2) and C(6, 6). Find : ...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the SHM is projection of uniform circular motion on the diam...
Text Solution
|
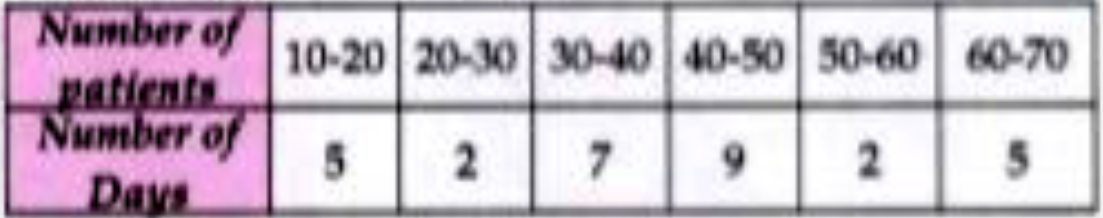
- The data on the number of patient attending a hospital in a month are ...
Text Solution
|
- Using properties of proportion solve for x, given (sqrt(5x)+sqrt(2x-...
Text Solution
|
- Sachin invests Rs. 8,500 in 10%, Rs. 100 shares at Rs. 170. He sells ...
Text Solution
|
- Sachin invests Rs. 8,500 in 10%, Rs. 100 shares at Rs. 170. He sells ...
Text Solution
|
- Sachin invests Rs. 8,500 in 10%, Rs. 100 shares at Rs. 170. He sells ...
Text Solution
|
- Use graph paper for this question. The marks obtained by 120 student...
Text Solution
|
- Use graph paper for this question. The amrks obtained by 120 student...
Text Solution
|
- Use graph paper for this question. The amrks obtained by 120 student...
Text Solution
|
- A man observes the angle of elevation of the top of the tower to be 45...
Text Solution
|
- Using the Remainder Theorem find the remainders obtained when x^(3)+(k...
Text Solution
|
- The product of two consecutive natural numbers which are multliples of...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, ABCDE is a pentagon inscribed in a circle such th...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, ABCDE is a pentagon inscribed in a circle such th...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, ABCDE is a pentagone inscribed in a circle such t...
Text Solution
|