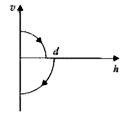
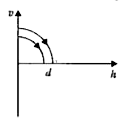
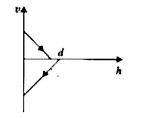
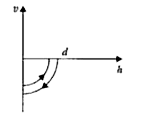
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
COMPETITION CARE UNIT
ICSE|Exercise Dynamics (PROJECTILE MOTION)|31 VideosCOMPETITION CARE UNIT
ICSE|Exercise Dynamics ( Laws of motion )|36 VideosCOMPETITION CARE UNIT
ICSE|Exercise VECTORS AND SCALARS [Selected from Previoius Years Engg. & Med. & IIT Exam Qns] |35 VideosCIRCULAR MOTION
ICSE|Exercise MODULE 2 (FROM ROTATIONAL KINETIC ENERGY , WORK ,POWER)|24 VideosDIMENSIONS
ICSE|Exercise SELECTED PROBLEMS (FROM CONVERSIONS OF ONE SYSTEMS OF UNITS INTO ANOTHER)|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ICSE-COMPETITION CARE UNIT-Dynamics (UNIFORMLY ACCELERATED MOTION)
- A body released from a great height and falls freely towards the earth...
Text Solution
|
- The ball is dropped from a bridge 122.5 m above a river, After the ba...
Text Solution
|
- A body dropped from a height h with initial velocity zero, strikes the...
Text Solution
|
- A body falling from the rest has a velocity v after it falls through a...
Text Solution
|
- A wooden block of mass 10 gm is dropped from the top of a cliff 100 m ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball A is thrown vertically upwards with speed u. At the same instan...
Text Solution
|
- A bomb is dropped from an aeroplane moving horizontal at constant spee...
Text Solution
|
- A stone is thrown vertically upwards. When stone is at a height half o...
Text Solution
|
- A bal is thrown vertically upwards from the ground. It crosses a point...
Text Solution
|
- A body, thrown upwards with some velocity, reaches the maximum height ...
Text Solution
|
- The height of a tower is h meter, A body is thrown from the top of tow...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped vertically from a height d above the ground. It hits...
Text Solution
|
- A man in a lift throws a ball vertically upwards with a velocity v and...
Text Solution
|
- A body falls freely form rest. It covers as much distance in the last ...
Text Solution
|
- A man throw rings into air one after the other at an interval of one s...
Text Solution
|
- A bird flies with a speed of 10 km/h and a car moves with uniform spee...
Text Solution
|
- A train of 150 m length is going towards north direction at a speed of...
Text Solution
|
- Two trains, each 50 m long are travelling in opposite direction with v...
Text Solution
|
- The first and the second runners in a 100 m dash have a gap of half me...
Text Solution
|
- Two stones are thrown from the same point with velocity of 5 ms^(-1) o...
Text Solution
|