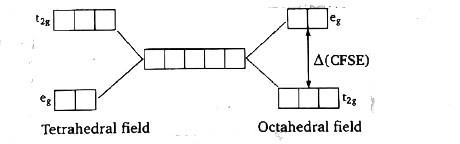
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise ONE OR MORE ANSWERS IS/ARE CORRECT|71 VideosCO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise MATCH THE COLUMN|36 VideosCO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL 2|144 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS|54 Videosd-BLOCK ELEMENTS
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS|32 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH-CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS-LEVEL 3 (PASSAGE TYPE)
- On the basic of stability of complex ion in the solution, complexes ma...
Text Solution
|
- When degenerate d-orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influenc...
Text Solution
|
- When degenerate d-orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influenc...
Text Solution
|
- When degenerate d-orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influenc...
Text Solution
|
- When degenerate d-orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influenc...
Text Solution
|
- When degenerate d-orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influenc...
Text Solution
|
- When degenerate d-orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influenc...
Text Solution
|
- When degenerate d-orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influenc...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic moment, ionic conductance and colligative properties are usef...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic moment, ionic conductance and colligative properties are usef...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic moment, ionic conductance and colligative properties are usef...
Text Solution
|
- The crystal field theory assumes interaction between metal ion and the...
Text Solution
|
- The crystal field theory assumes interaction between metal ion and the...
Text Solution
|
- The crystal field theory assumes interaction between metal ion and the...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic property, dipole moment, plane of symmetry, colour and ab...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic property, dipole moment, plane of symmetry, colour and ab...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic property, dipole moment, plane of symmetry, colour and ab...
Text Solution
|
- Ligands are broadly classified into two classes classical and non-clas...
Text Solution
|
- Ligands are broadly classified into two classes classical and non-clas...
Text Solution
|
- Ligands are broadly classified into two classes classical and non-clas...
Text Solution
|