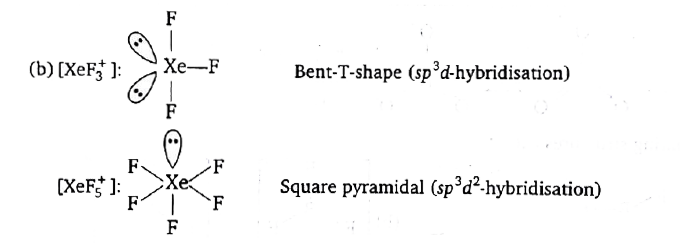A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise Level 2|62 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise Level 3 (Passive 1)|6 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING (ADVANCED)
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS|64 VideosCO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL 2|144 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH-CHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)-SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS
- SbF(5) reacts with XeF(4) and XeF(6) to form ionic compounds [XeF(3)^(...
Text Solution
|
- Consider following compounds A to E : (A) XeF(n) " " (B) XeF((n+1)...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following five group (According to modern periodic table)...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following species and find out total number of species wh...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following table regarding interhalogen compounds, XY(n) (...
Text Solution
|
- What is covalency of chlorine atom in second excited state ?
Text Solution
|
- Sum of sigma and pi bonds in NH(4)^(+) cation is ..
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the value of X-Y, for XeOF(4). (X=Number of sigma bond pair ...
Text Solution
|
- The molecule ABn is planar with six pairs of electrons around A in the...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate value of (X+Y+Z)/(10), here X is O-N-O bond angle in NO(3)^(...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate x+y+z for H(3)PO(3) acid, where x is no. of lone pairs, y is...
Text Solution
|
- How many right angle, bond angles are present in TeF(5)^(-) molecular ...
Text Solution
|
- How may possible angle FSeF bond angles are present in SeF(4) molecule...
Text Solution
|
- In IF(6)^(-) and TeF(5)^(-), sum of axial d-orbitals which are used in...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following, total no. of planar species is : (i) SF(4) " "...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the value of " x+y-z" here x,y and z are total number of non...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following table Then calculate value of "p+q+r-s-t".
Text Solution
|
- In phosphorus acid, if X is number of non bonding electron pairs. Y is...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the number of p(pi)-d(pi) bond(s) present in SO(4)^(2-) :
Text Solution
|
- Sum of sigma and pi bonds in NH(4)^(+) cation is ..
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following orbitals (i)3p(x) (ii)4d(z^(2)) (iii)3d(x^(2)...
Text Solution
|