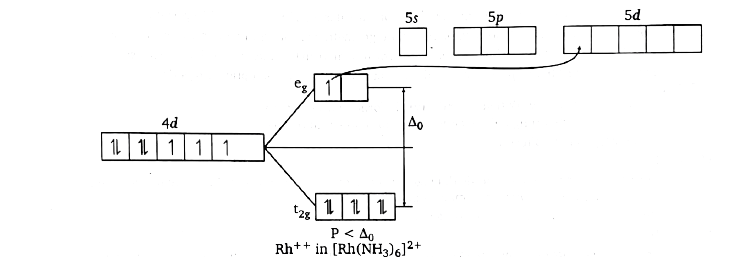
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise ONE OR MORE ANSWERS IS/ARE CORRECT|71 VideosCO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise MATCH THE COLUMN|36 VideosCO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL 2|144 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS|54 Videosd-BLOCK ELEMENTS
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS|32 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH-CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS-LEVEL 3 (PASSAGE TYPE)
- An isomerr of the complex CoBrCl(2)(en)(2)(H(2)O), on reaction with co...
Text Solution
|
- Crystal field theory provides correct electronic distribution of centr...
Text Solution
|
- Crystal field theory provides correct electronic distribution of centr...
Text Solution
|
- Crystal field theory provides correct electronic distribution of centr...
Text Solution
|
- Two important physical evidences supporting the synergic bonding in no...
Text Solution
|
- Two important physical evidences supporting the synergic bonding in no...
Text Solution
|
- Two important physical evidences supporting the synergic bonding in no...
Text Solution
|
- Complex compounds that have the same molecular formula but have differ...
Text Solution
|
- Complex compounds that have the same molecular formula but have differ...
Text Solution
|
- Complex compounds that have the same molecular formula but have differ...
Text Solution
|
- A complex compound of chromium chromium contains five NH(3) molecules,...
Text Solution
|
- A complex compound of chromium chromium contains five NH(3) molecules,...
Text Solution
|
- A complex compound of chromium chromium contains five NH(3) molecules,...
Text Solution
|
- According to C.F.T, attraction between the central metal ion and ligan...
Text Solution
|
- According to C.F.T, attraction between the central metal ion and ligan...
Text Solution
|
- According to C.F.T, attraction between the central metal ion and ligan...
Text Solution
|
- An isomer of the complex Co(en)(2)(H(2)O)IC l(2), on reaction with con...
Text Solution
|
- An isomer of the complex Co(en)(2)(H(2)O)IC l(2), on reaction with con...
Text Solution
|
- An isomer of the complex Co(en)(2)(H(2)O)IC l(2), on reaction with con...
Text Solution
|
- In complexes off wea field ligands, Delta(o) lt P (pairing energy), th...
Text Solution
|