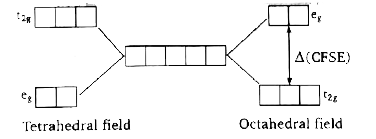A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise ONE OR MORE ANSWERS IS/ARE CORRECT|71 VideosCO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise MATCH THE COLUMN|36 VideosCO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL 2|144 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS|54 Videosd-BLOCK ELEMENTS
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS|32 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH-CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS-LEVEL 3 (PASSAGE TYPE)
- An isomer of the complex Co(en)(2)(H(2)O)IC l(2), on reaction with con...
Text Solution
|
- An isomer of the complex Co(en)(2)(H(2)O)IC l(2), on reaction with con...
Text Solution
|
- An isomer of the complex Co(en)(2)(H(2)O)IC l(2), on reaction with con...
Text Solution
|
- In complexes off wea field ligands, Delta(o) lt P (pairing energy), th...
Text Solution
|
- In complexes off wea field ligands, Delta(o) lt P (pairing energy), th...
Text Solution
|
- In complexes off wea field ligands, Delta(o) lt P (pairing energy), th...
Text Solution
|
- Complex compounds are molecular compounds which retain their identitie...
Text Solution
|
- Complex compounds are molecular compounds which retain their identitie...
Text Solution
|
- Complex compounds are molecular compounds which retain their identitie...
Text Solution
|
- Recent X-ray work, IR and other spectroscopic methods have proved that...
Text Solution
|
- Recent X-ray work, IR and other spectroscopic methods have proved that...
Text Solution
|
- On the basic of stability of complex ion in the solution, complexes ma...
Text Solution
|
- On the basic of stability of complex ion in the solution, complexes ma...
Text Solution
|
- When degenerate d-orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influenc...
Text Solution
|
- When degenerate d-orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influenc...
Text Solution
|
- When degenerate d-orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influenc...
Text Solution
|
- When degenerate d-orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influenc...
Text Solution
|
- When degenerate d-orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influenc...
Text Solution
|
- When degenerate d-orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influenc...
Text Solution
|
- When degenerate d-orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influenc...
Text Solution
|