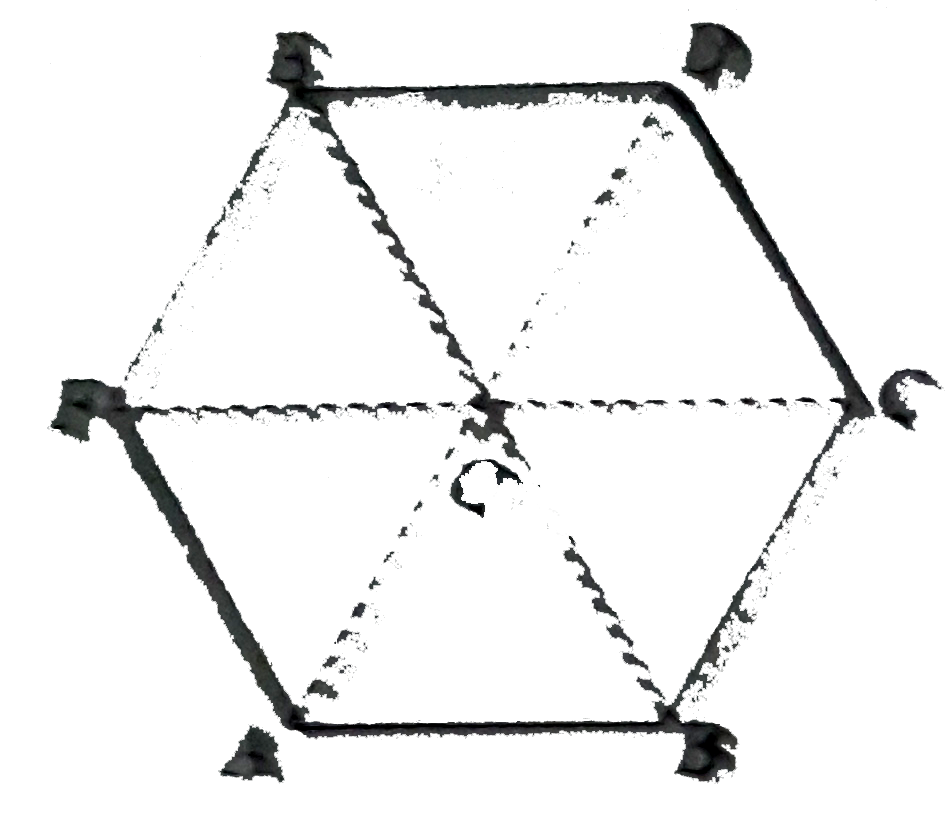
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-VECTORS-Exercise Single Correct
- Mark the correct statement.
Text Solution
|
- Out of the following forces, the resultant of which cannot be 10N?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following pairs of forces cannot be added to give a resul...
Text Solution
|
- In an equilateral triangle ABC, AL, BM, and CN are medians. Forces alo...
Text Solution
|
- The sum of two vectors A and B is at right angles to their difference....
Text Solution
|
- If a parallelogram is formed with two sides represented by vector vec(...
Text Solution
|
- Given that vec(A)+vec(B)=vec(C ) and that vec(C ) is perpendicular to ...
Text Solution
|
- Two forces vec(F)(1)=500N due east and vec(F)(2)=250N due north have t...
Text Solution
|
- Find the resultant of the three vectors vec(OA), vec(OB) and vec(OC) s...
Text Solution
|
- Two vectors vec(a) and vec(b) are at an angle of 60^(@) with each othe...
Text Solution
|
- The resultant of two vectors vec(P) and vec(Q) is vec(R). If vec(Q) is...
Text Solution
|
- A vector vec(A) When added to the vector vec(B)=3hat(i)+4hat(j) yields...
Text Solution
|
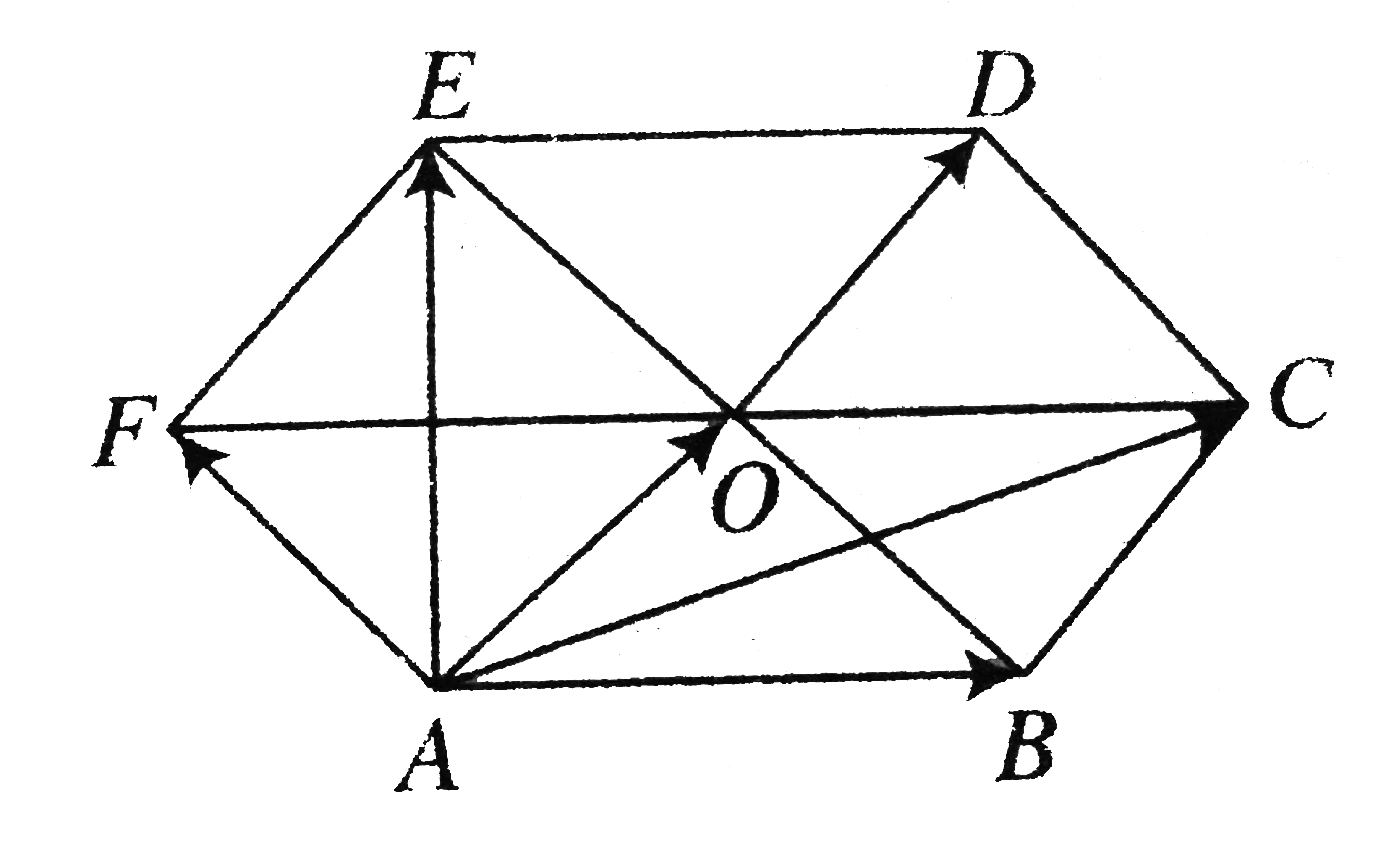
- IN the figure shown ,ABCDEF is a regular hexagon . What is the of AB+A...
Text Solution
|
- In a two diamensional motion of a particle, the particle moves from po...
Text Solution
|
- The sum of two forces at a point is 16N. if their resultant is normal...
Text Solution
|
- The angle between two vector A and B is theta. Vector R is the resulta...
Text Solution
|
- The resultant of three vectors 1,2, and 3 units whose directions are t...
Text Solution
|
- A unit vector along the incident ray of light is hat(i). The unit vect...
Text Solution
|
- The components of a vector along the x- and y- directions are (n+1) an...
Text Solution
|
- Two point masses 1 and 2 move with uniform velocities vec(v)(1) and ve...
Text Solution
|