Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Examples|11 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 6.1|11 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|10 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer type|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1-Integer
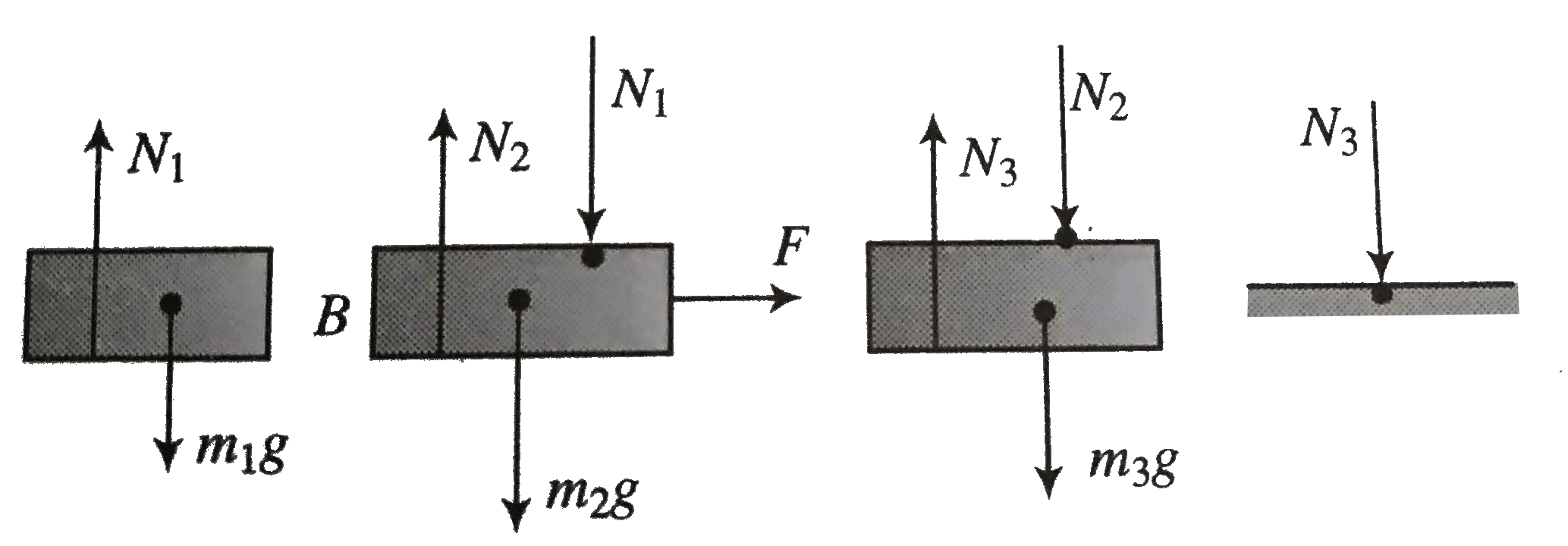
- Three block A,B,and C of mass m(1),m(2) and m(3), respectively are res...
Text Solution
|
- A block is placed on an inclined plane moving towards right horizontal...
Text Solution
|
- You are designing an elevator for a hospital. The force exerted on a p...
Text Solution
|
- Figure represents a painter in a crate which hangs alongside a buildin...
Text Solution
|
- The elevator shown in fig. is descending with an acceleration of 2ms^(...
Text Solution
|
- In fig. find the acceleration of B if acceleration of A is 2ms^(-2).
Text Solution
|