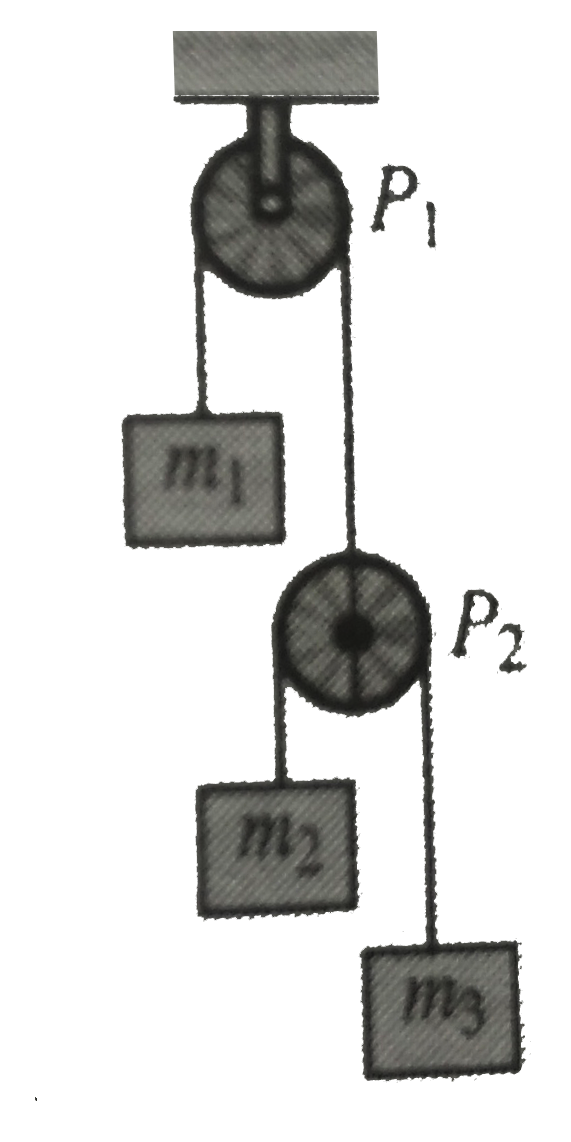
Constraint relations Method 1:
For the upper string, the length of string `l_(1)` not to change and for this string not to slacken, acceleration of `m_(1)` w.r.t. the fixed pulley = acceleration of the movable pulley w.r.t. the fixed pulley
or `|a_(1)|=|a_(P)|` ..(i)
Constraint relations for string 2
Let us assume that block `m_(1)` is moving down with acceleration `a_(2)` and `a_(3)` , respectively w.r.t. ground
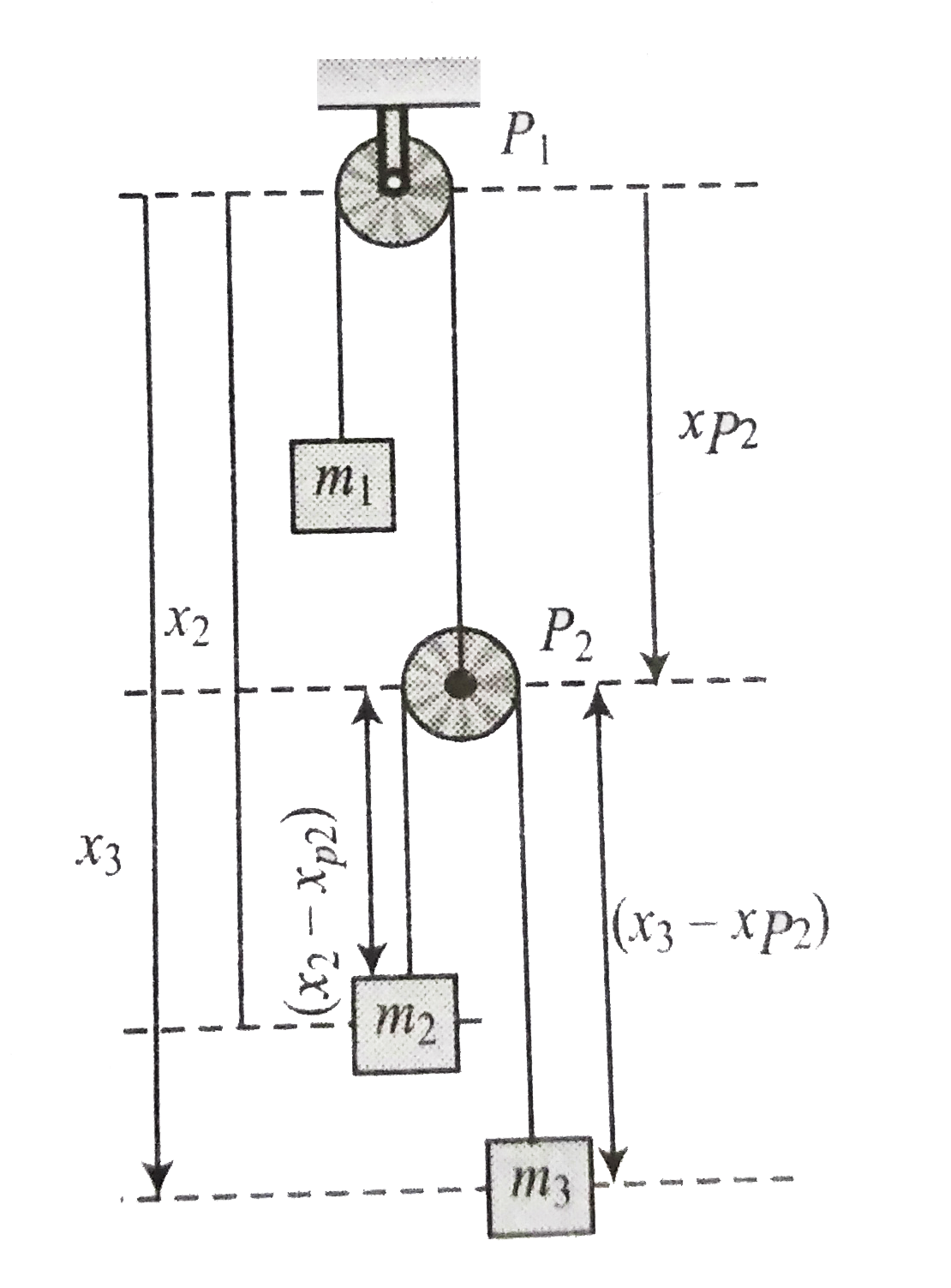
Total length of string 2 is constant. Therefore,
`l_(2)=(x_(2)-x_(p_2))+(x_(3)-x_(p_2))+l'_(0)`
where `l_(0)` is the length of string on pulley 2 passing through the pulley `P_(2)`
`l_(2)=x_(2)+x_(3)-2x_(P_2)+l'_(0)`...(ii)
Differentiating Eq. (ii) w.r.t. time
`(dl^(2))/(dt) = 0` (as total length of string is constanat)
`(dl'_(0))/(d)=0` (as length of string over pulley is constant)
differentiating eq.(ii) twice w.r.t. time
`2a_(1)=a_(3)+a_(2)` ..(iii)
Method 2: The acceleration of block `m_(1)` and pulley 2 will be same in magnitude. Now considering pulley 2 and block 2 and 3.
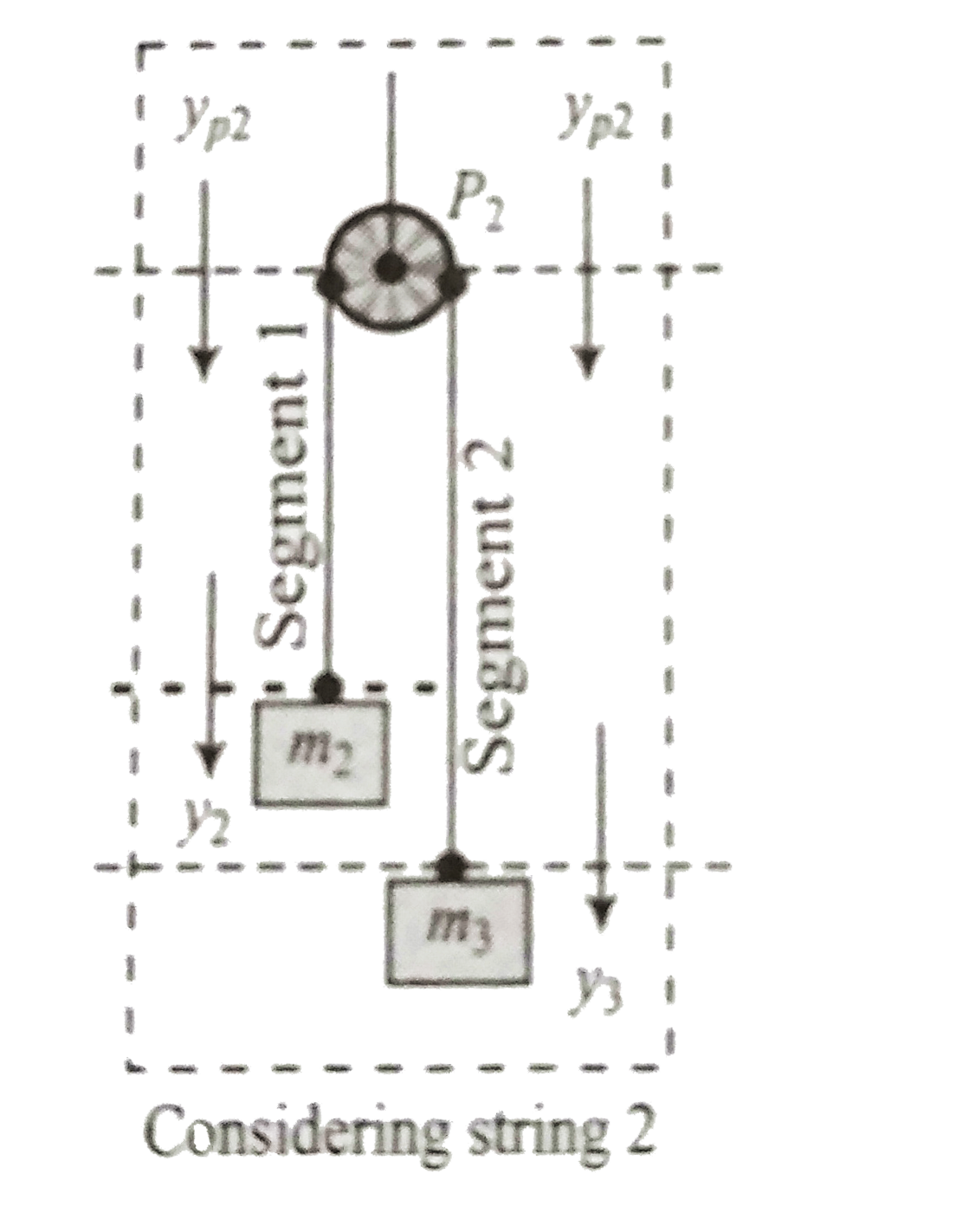
Change in the length of segment (1)
`Delta l_(1)=(+y_(2))+(-y_(P_2))=y_(2)-y_(p_2)`
Change in the length of segment (2)
`Delta l_(2)=(y_3)+(-y_(p_2))=y_(3)-y_(P_2)`
Total sum of change in the segment length of string should be zero.
`Delta l =0 = [y_(2)-y_(P_2)]+[y_(2)-y_(P_2)]`
`implies Delta l = 0 =y_(2)+y_(3)-2y_(P_2)`
`implies2y_(p_2)=y_(3)+y_(2) implies 2a_(p_2)=a_(3)+a_(2)`
or `2 a_(1)=a_(3)+a_(2)`
This equation is same as (iii) calculate in method (2) .
Method 3: For the rope length `l_(2)` not to change and for this rope not to slacken acceleration of `m_(2)` w.r.t movable pully =-acceleration of `m_(3)`w.r.t. movable pullwy
or `(a_(2)-a_(p))=-(a_(3)-a_(p))`
`a_(2)+a_(3)-2a_(p)=0 implies 2a_(0)=a_(2)+a_(3)`
This equation is same as Eq.(iii) as calucutate in method 1 and 2
Applying Newton's laws of motion equations.
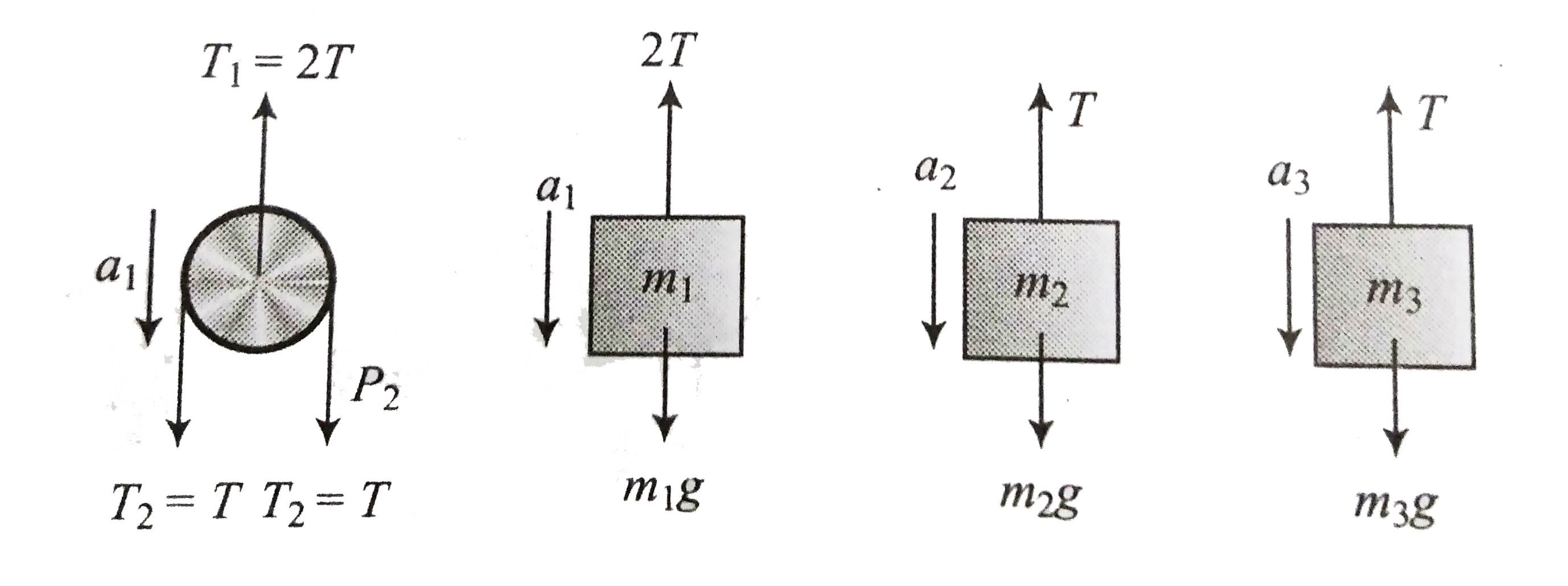
Free body diagram
Equation of motion
for `m_(1): 2T-m_(1)g=m_(1)a_(1)` ...(iv)
for `m_(2):m_(2)g-T=m_(2)a_(2)`...(v)
for `m_(3):m_(3)g-T=m_(3)a_(3)`...(vi)
After solving (iii),(iv), (v), and (vi), we get
`a_(1)=(4m_(2)m_(3)g-m_(1)(m_(2)+m_(3))g)/(4m_(2)m_(3)+m_(1)(m_(2)+m_(3)))`.