Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 6.4|13 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|15 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 6.2|35 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|10 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer type|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1-Exercise 6.3
- Block A is given an acceleration 12 ms^(-2) towards left as shown in f...
Text Solution
|
- The three block shown in fig. move with constant velocities. Find the ...
Text Solution
|
- For the system as shown in fig. find the acceleration of C. the accele...
Text Solution
|
- System is shown in fig. and wedge is moving toward left with speed 2ms...
Text Solution
|
- In fig. shown, the speed of the truck is v to the right. Find the spee...
Text Solution
|
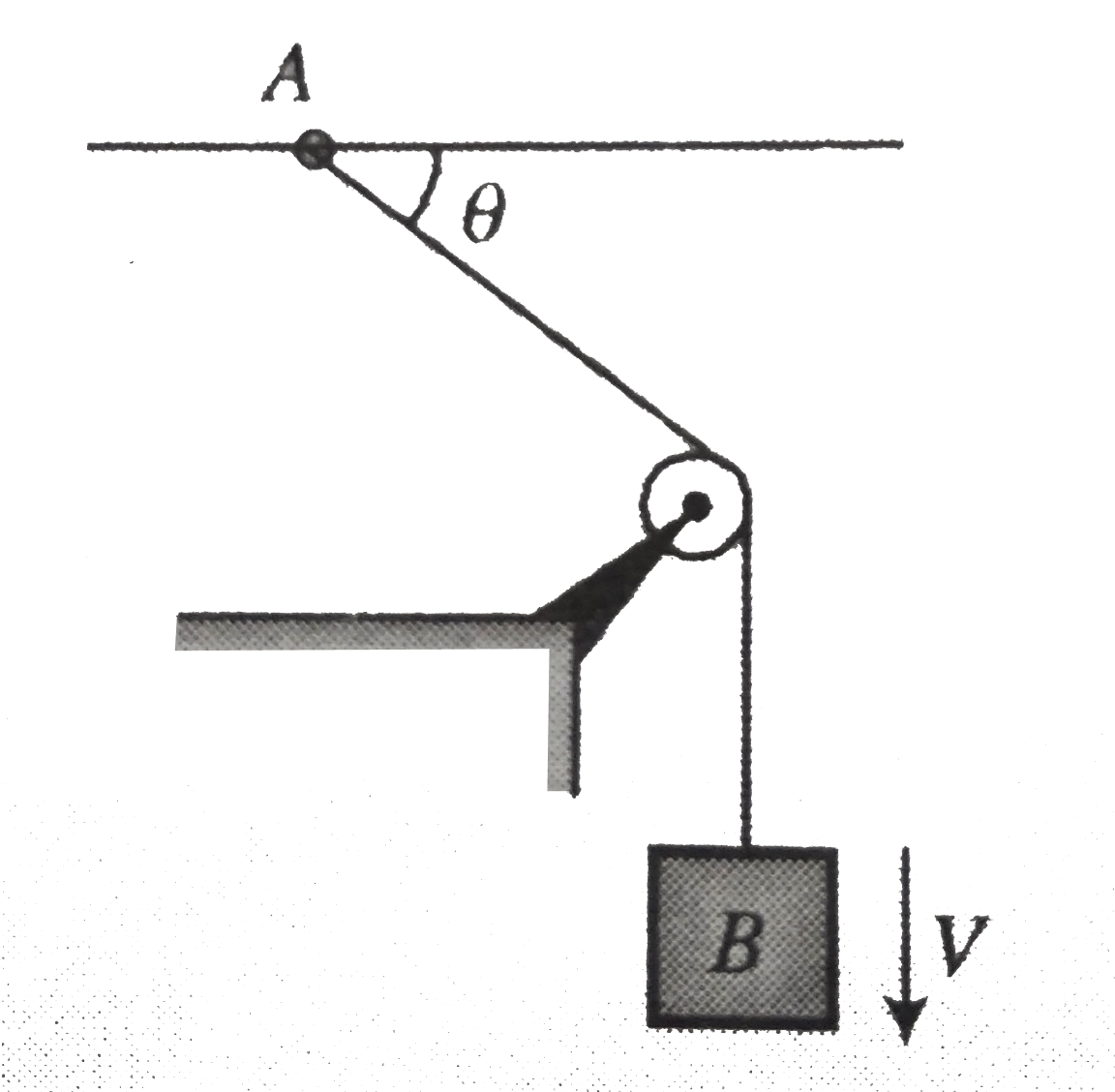
- Determine the speed with which block B rises in fig. if the end of the...
Text Solution
|
- An inextensible string AB is tied to a block B of negligible dimension...
Text Solution
|
- Find the acceleration of blocks in fig. The pulley and the string are...
Text Solution
|
- In the pulley-block arrangement shown in figure , find the relation be...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a pulley over which is string passes and connected to two...
Text Solution
|
- Find the relation in the accelerations of the three masses shown in fi...
Text Solution
|
- A ring A which can slide on a smooth wire is connected to one end of a...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a block A constrained to slide along the inclined plane o...
Text Solution
|
- Find the acceleration of block B as shown in fig. (a) and (b) relative...
Text Solution
|
- If the string is inextensible, determine the velocity u of each block ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the acceleration of block A and B in cases (a),(b), and (c )...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of mass m is supported on a wedge of mass M shown in fig. Find t...
Text Solution
|
- In fig, no relative motion takes place between the wedge and the block...
Text Solution
|
- The velocities of A and B shown in fig. Find the speed (in ms^(-1)) of...
Text Solution
|