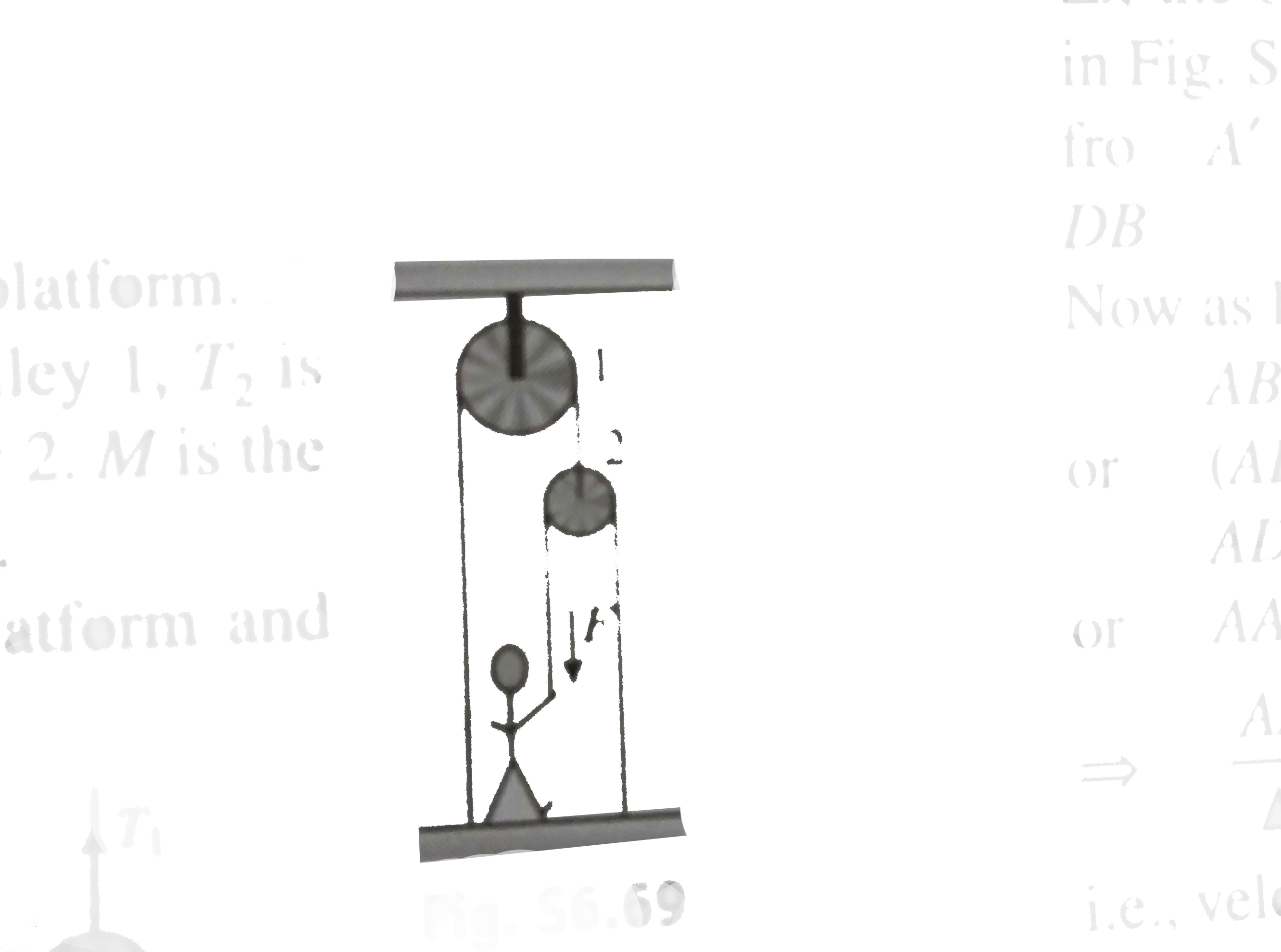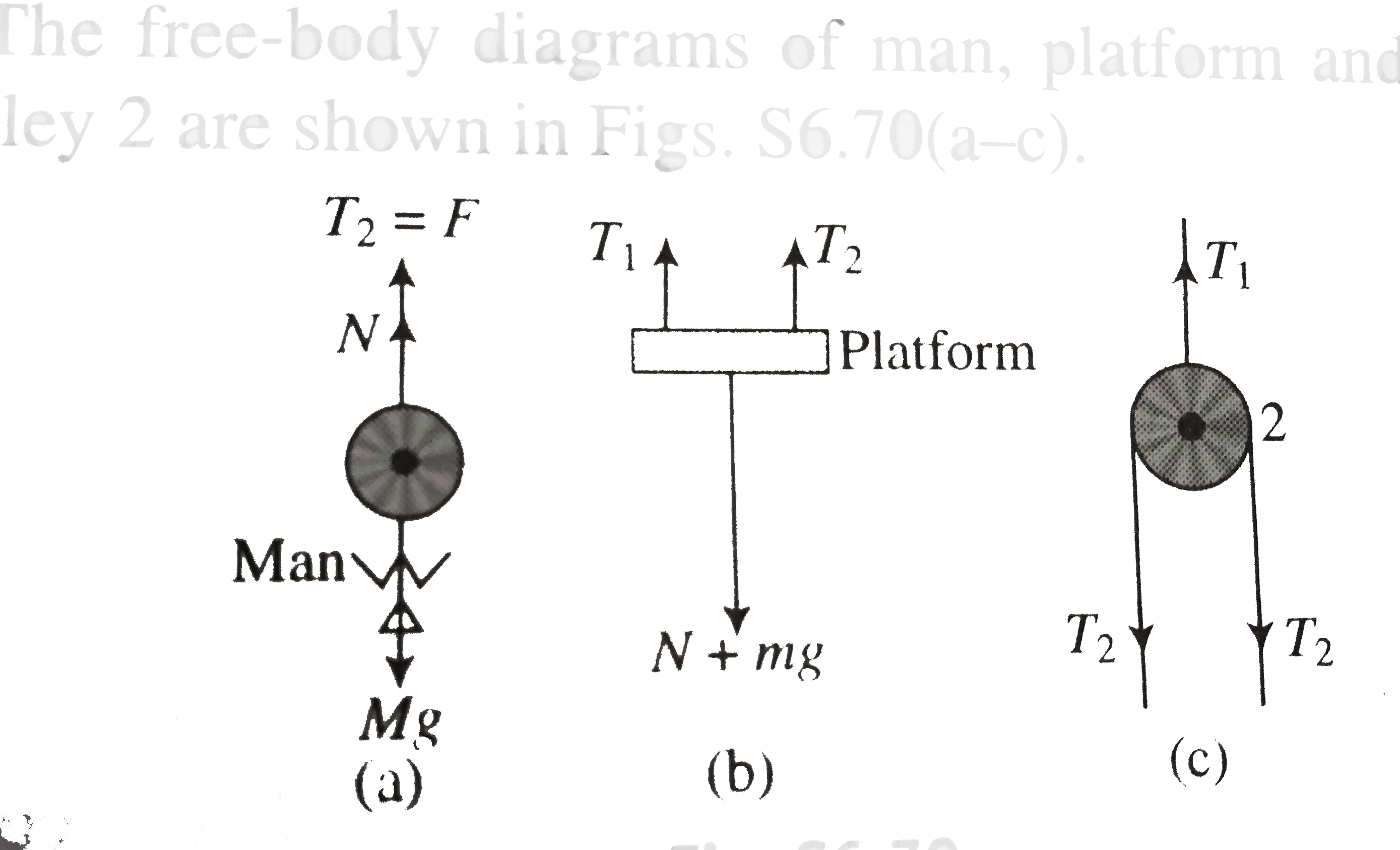Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Single Correct|75 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|11 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 6.4|13 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|10 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer type|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1-Subjective
- A hot- air balloon consists of a basket, one passenger, and some carge...
Text Solution
|
- A student tries to raise a chain consisting of three identical links. ...
Text Solution
|
- Two men of masses M and M+m start simultaneously from the ground and c...
Text Solution
|
- In fig. the man and the platform together weight 950N. The pulley can ...
Text Solution
|
- The monkey B shown in figure is holding on to the tail of the monkey A...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth ring A of mass m can slide on a fixed horizontal rod. A strin...
Text Solution
|
- A particle A of mass 2m is held on a smooth horizontal table and is at...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth pulley A of mass M(0) is lying on a frictionless table. A mas...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is at rest relative to the stationary wedge of mass ...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in fig., all pulleys are smooth and massless....
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a block of mass m(1) sliding on a block of mass m(2), wit...
Text Solution
|
- The system shown in fig. is given an acceleration a towards left. Assu...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in fig. a wedge of mass m(3) =3.45 kg is plac...
Text Solution
|
- In the system shown in fig., m(A)=4m, m(B)=3m, and m(c)=8m. Friction i...
Text Solution
|
- The system shown in fig, is released from rest. Calculate the tension ...
Text Solution
|