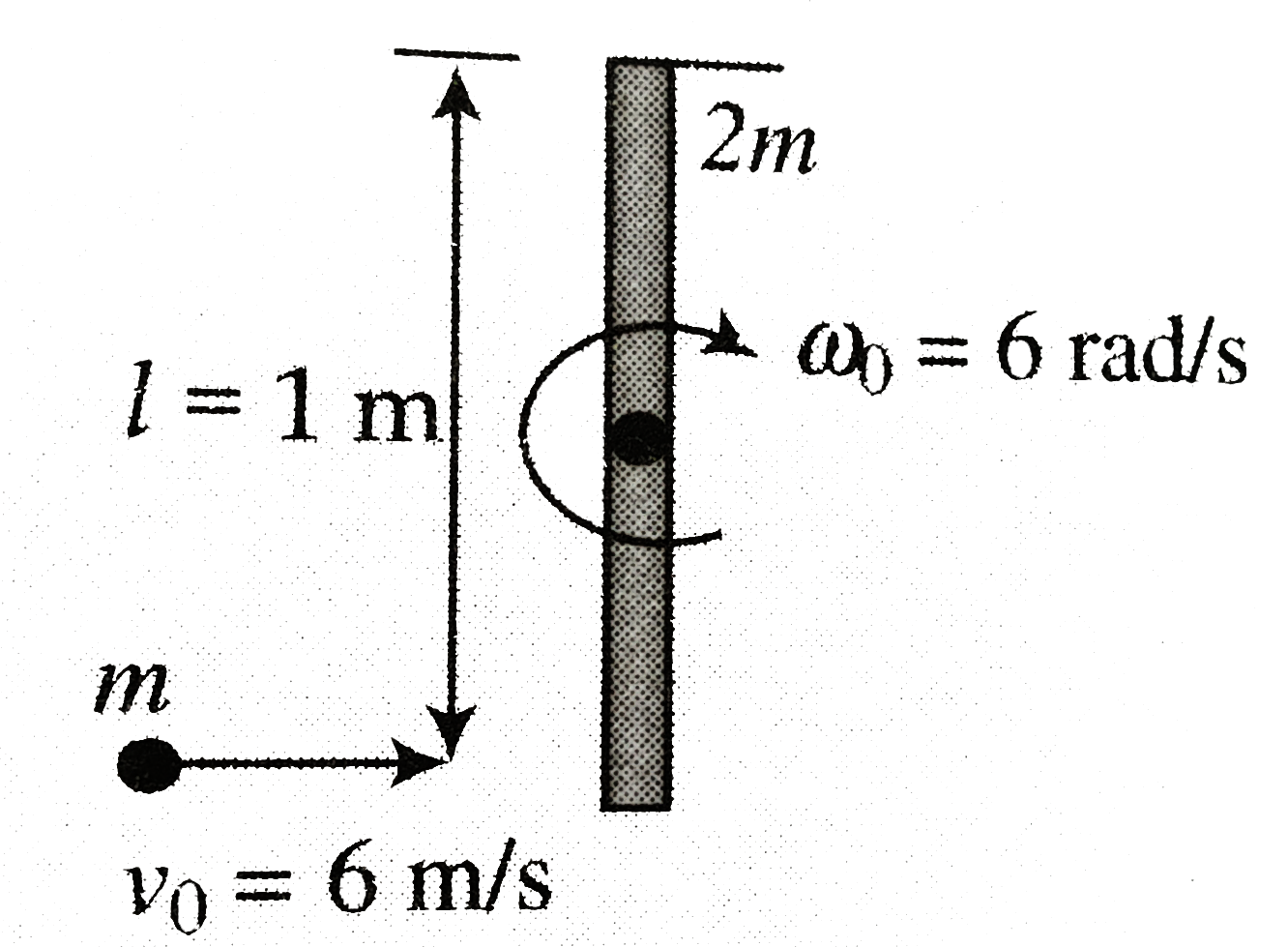The impulse acting on the rod -bullet system during the impact is shown in figure. `J_(1)` is the impulse acting on the rod by the hinge. Here the role of `J_(1)` is a little intersecting force. `J` could be greater than zero `J_(1)gt0, F_(1)` could be equal to zero, `J_(1)=0`, and `F_(1)` could be less than zero `J_(1)lt0`. And as a consequence the linear momentum of the system may increase, may remain constant or may decrease.

a. During the impact, the moment ofimpulse acting o the rod bullet system ahout the hinge is zero. Angular momentum about the hine will remain constant. Let `omega` be the angular velocity of the system about the hinge.
`["Angular momentum of the system"]_("initial")=["Angular momentum of the system"]_("final") `
`implies mvxxl=I_(0)xxomega`......i
Where `I_(0)` is the moment of inertia of the rod bullet system after collision about `O`
`I_(0)=I_("rod")+I_("bullet")=1/3Ml^(2)+ml^(2)`.....ii
`mvl=(1/3Ml^(2)+ml^(2))omega`..............iii
As the system swings about hinge, the mechanical energy of the system will remain constant `/_\k+/_\U=0`
`[1/2(1/3Ml^(2)+ml^(2))omega^(2)-0]`
`=mgl/2(1-cosalpha)+mg(1-cosalpha)`
From eqn iii `omega=(3mv)/(l(M+3m))`............iv
Substituting this value of `omega` in eqn `v` we get
`1/2(1/3Ml^(2)+ml^(2))((3mv)/(l(M+3m)))^(2)`
`implies 1/2xx1/2l^(2)(M+3m)(9m^(2)v^(2))/(l^(2)(M+3m)^(2))`
`=gl(1-cosalpha)/2(M+2m)`
`implies v^(2)=(2gl)/3((M+2m)(M+3m))/m^(2)sin^(2)alpha/2`
Now for `mltltm, (M+3m)(M+3m)~~M^(2)`
Thus `v^2=2/3gl(M^(2))/(m^(2))sin^(2)alpha/2impliesv=M/msqrt(2/3gl)sinalpha/2`
b. Change in linear momentum during the impact
`implies /_\p=p_(f)-p_(i)`
`={M(l/2omega)+m(lomega)}-mv`
`=kl((M+2m)/2)omega-mv`.........v
From eqn iv and i
`=l((M+2m)/2)(3mv)/(l(M+3m))-mv`
`=3/2mv-mv=1/2mv`
`=1/2m M/msqrt(1/2)gl sinalpha/2`
`=Msqrt(1/6)glsinalpha/2`
what causes linear momentum to change? Obviously, impulse `J_(1)` at hinge. Here `/_\p` is positive, linear momentum increase so `J_(1)` must be towards the right.