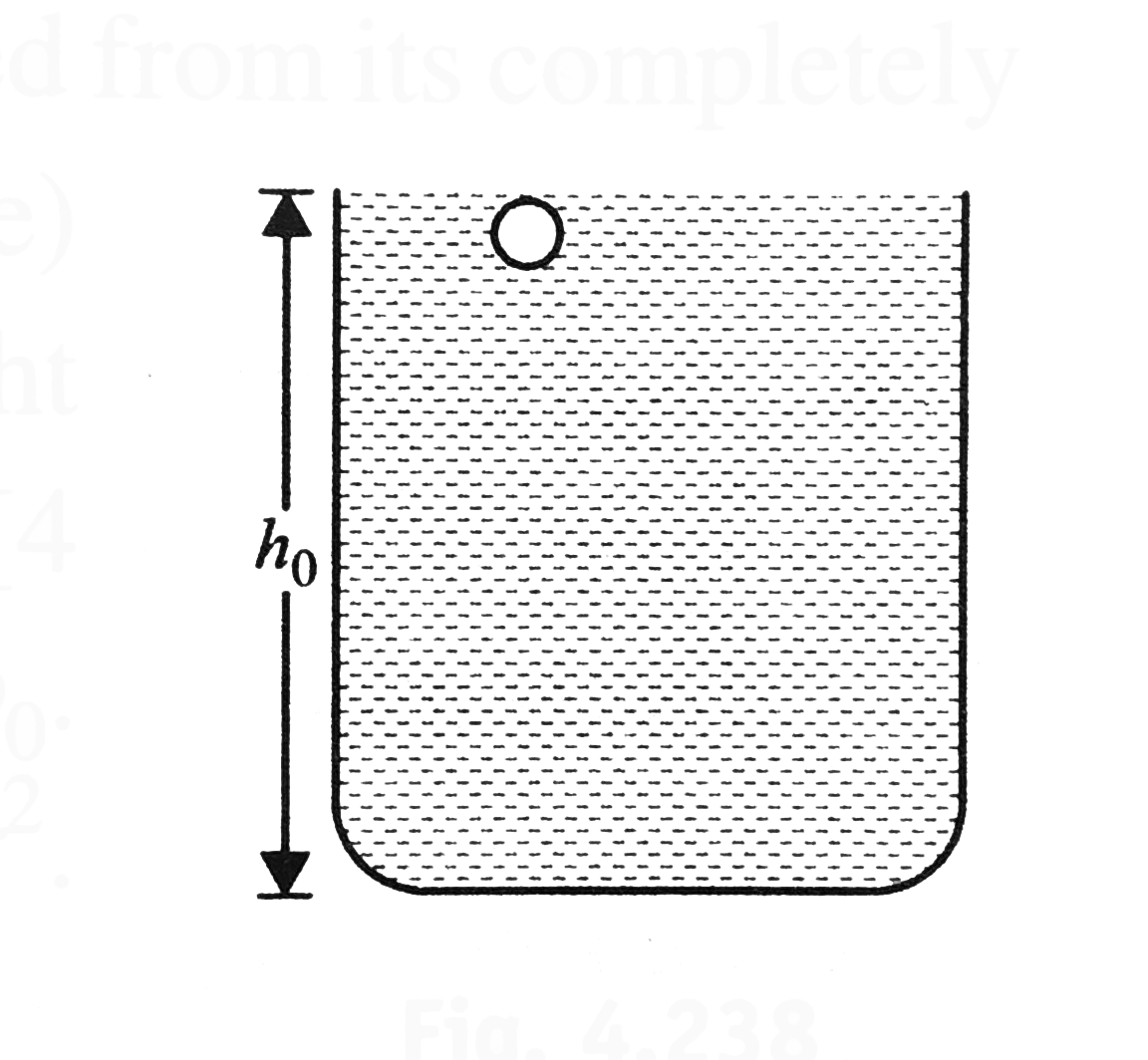
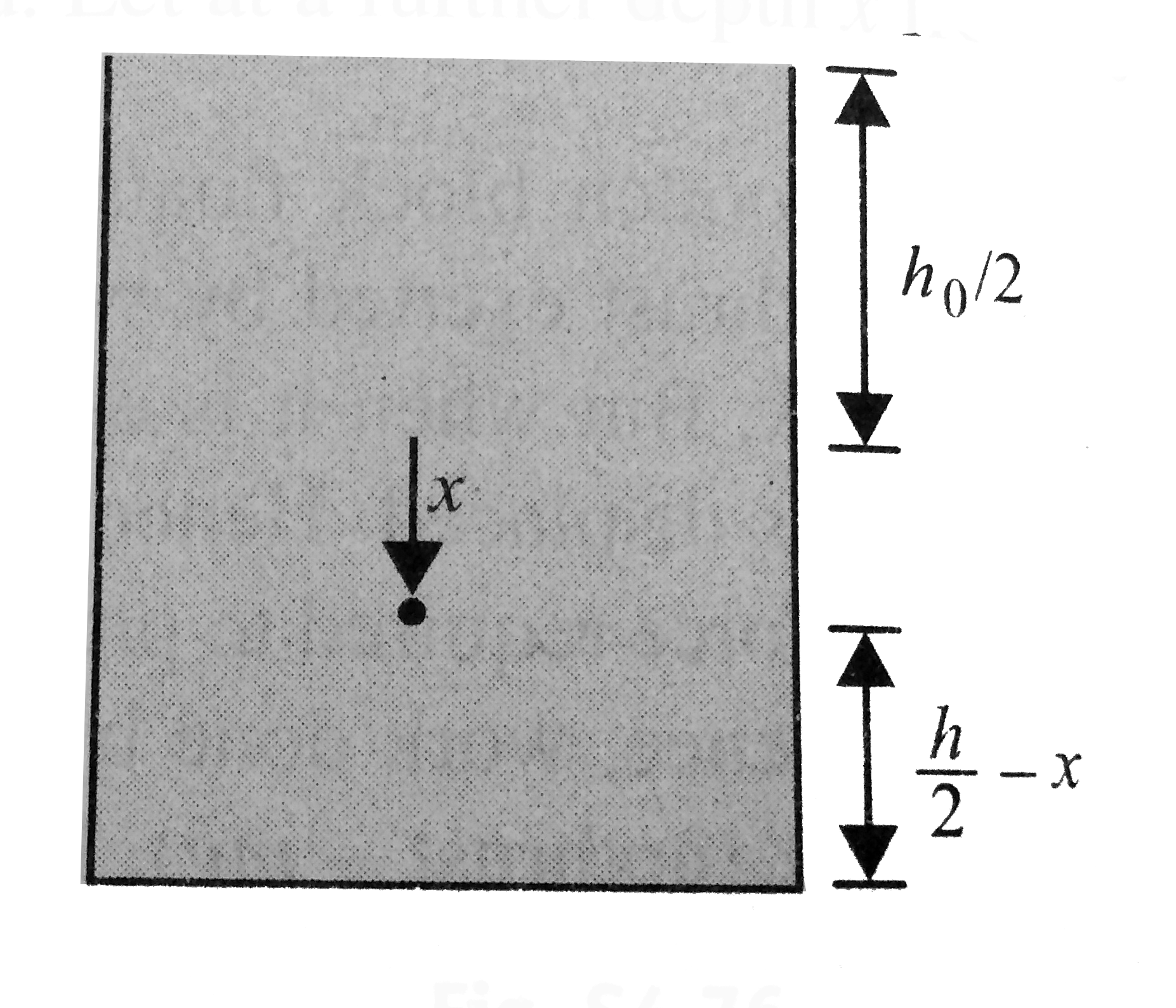
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
FLUID MECHANICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Linked Comprehension|43 VideosFLUID MECHANICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise True/False|1 VideosFLUID MECHANICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multipe Correct|15 VideosDIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|2 VideosGRAVITATION
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-FLUID MECHANICS-Assertion-Reasoning
- Assertion: Pascal law is the working principle of hydraulic lift. Re...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: In taking into account the fact that any object, which floa...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: A dam for water reservoir is built thicker at bottom than a...
Text Solution
|
- Statement I: In the three cases shown in the figure, force exerted by ...
Text Solution
|
- Statement 1 : The velocity increases, when water flowing in broader pi...
Text Solution
|
- Statement I: When spinning ball is thrown it deviates from its usual p...
Text Solution
|
- Statement I: A liquid will flow faster and more smoothly from a sealed...
Text Solution
|
- A small spherical ball of radius r is released from its completely sub...
Text Solution
|