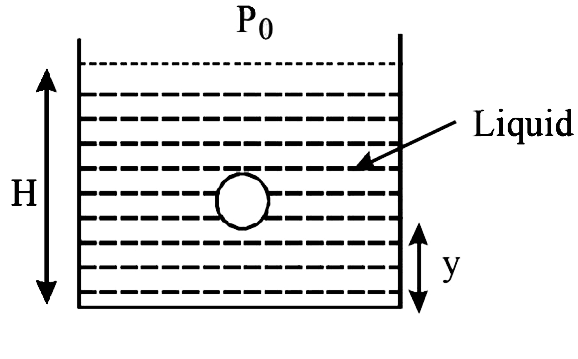
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-FLUID MECHANICS-LC_TYPE
- A cylindrical tank has a hole of diameter 2r in its bottom. The hole i...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical tank has a hole of diameter 2r in its bottom. The hole i...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical tank has a hole of diameter 2r in its bottom. The hole i...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed thermally conducting cylinder has a radius R and height L0. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed thermally conducting cylinder has a radius R and height L0. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed thermally conducting cylinder has a radius R and height L0. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A small spherical monoatomic ideal gas bubble (gamma=5//3) is trapped ...
Text Solution
|
- A small spherical monoatomic ideal gas bubble (gamma=5//3) is trapped ...
Text Solution
|
- A small spherical monoatomic ideal gas bubble (gamma=5//3) is trapped ...
Text Solution
|