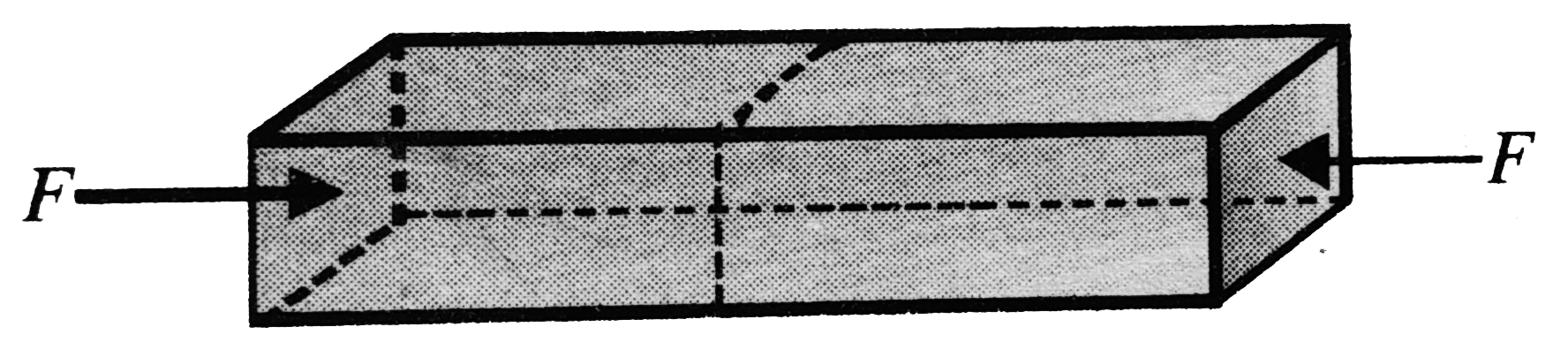
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|17 VideosPROPERTIES OF SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion- Reasoning|13 VideosPROPERTIES OF SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|16 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer type|1 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS AND FLUIDS-Single Correct
- A glass rod of radius 1 mm is inserted symmetrically into a glass capi...
Text Solution
|
- Two soap bubbles A and B of different diameters are blown at the two e...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, forces of equal magnitude are applied to the two ...
Text Solution
|
- The space between two large horizontal metal plates, 6 cm apart, is fi...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure that has to be applied to the ends of a steel wire of l...
Text Solution
|
- Maximum excess pressure inside a thin-walled steel tube of radius r an...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal and opposite point forces applied at mid- points of the ends...
Text Solution
|
- A 5 kg rod of square cross section 5 cm on a side and 1m long is pulle...
Text Solution
|
- If two soap bubbles of different radii are connected by a tube
Text Solution
|
- A paper disc of radius R from which a hole of radius r is cut out is f...
Text Solution
|
- A glass rod of radius 1 mm is inserted symmetrically into a glass capi...
Text Solution
|
- The elastic limit of an elavator cable is 2xx10^(9)N//m^(2). The maxim...
Text Solution
|
- A wire can sustain the weight of 20 kg before breaking. If the wire is...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length L and radius r is clamped rigidly at one end. When th...
Text Solution
|
- On applying a stress of xN//m^(2), the length of wire of some material...
Text Solution
|
- A copper and a steel wire of the same diameter are connectedend toend....
Text Solution
|
- A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 xx 10^(-5)"...
Text Solution
|
- The edge of an aluminium cube is 10 cm long. One face of the cube is f...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of radius r made of a soft material of bulk modulus K i...
Text Solution
|
- A film of water is formed between two straight parallel wires each 10c...
Text Solution
|