Let `P` be the point on the joining the centres of the two planets such that the net field at that point is zero.
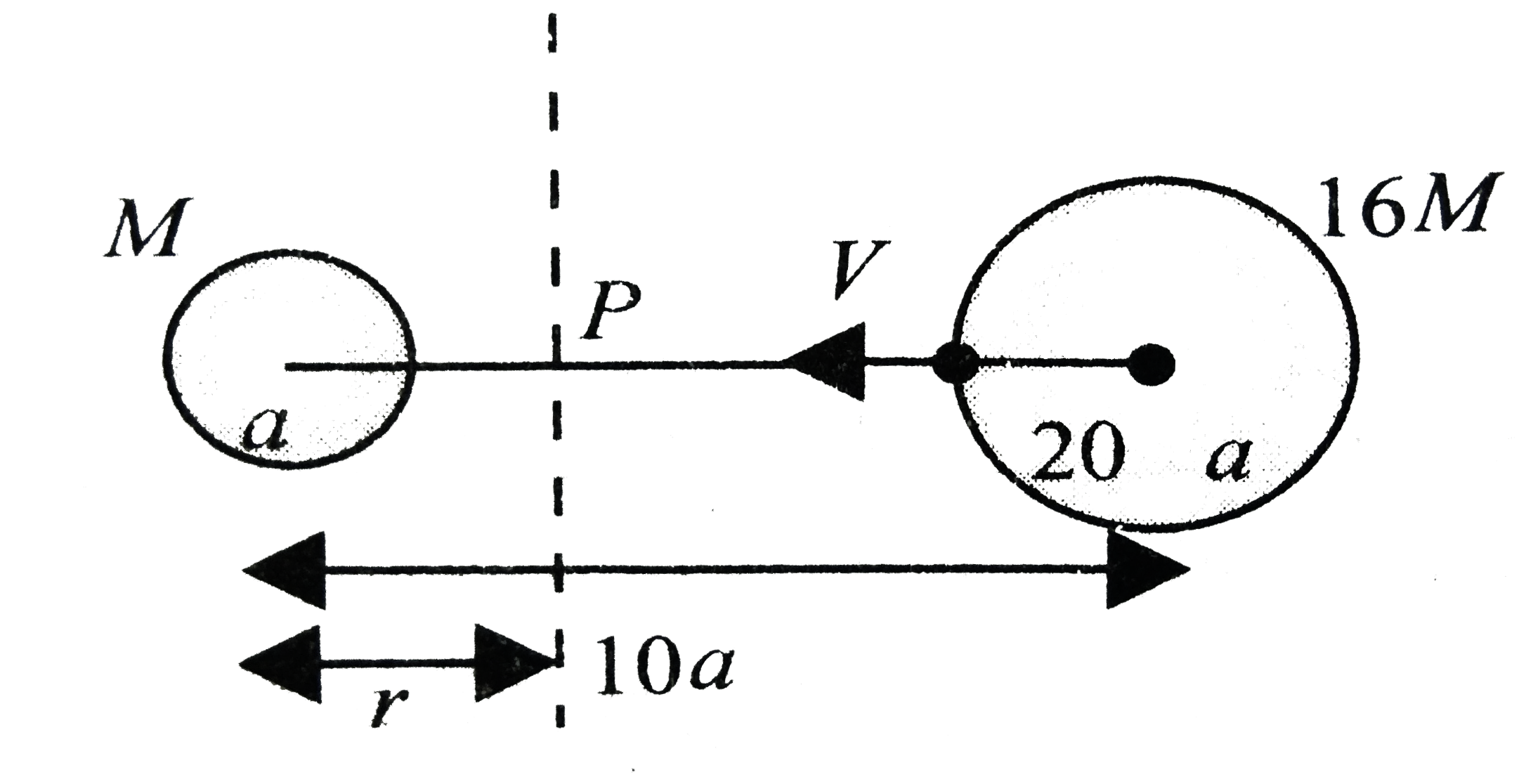
Then `(GM)/(r^(2))-(G16M)/((10a-r)^(2))=0`
`implies(10a-r)^(2)=16r^(2)`
`implies 10a-r=4r`
`impliesr=2a`
Potential at point `P`
`v_(P)=(-GM)/r=(G16M)/((10a-r))=(-GM)/(2a)-(2GM)/a`
`(-5GM)/(2a)`
Now if the particle projected from the larger planet has enough energy to cross this point, it will reach the smaller planet.
For this, the `KE` imparted to the body must be just enough to raise its total mechanical enrgy to a value which is equal to `PE` at point `P`, i.e.
`1/2mv^(2)-(G(16M)m)/(2a)-(GMm)/(8a)=mv_(P)`
or `(v^(2))/2-(8GM)/a-(GM)/(8a)=(5GMm)/(2a)`
or `v^(2)=(45GM)/(4a)`
or `v_(min)=3/2sqrt((5GM)/a)`