Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
COULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective Type|15 VideosCOULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|32 VideosCOULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved examples|10 VideosCENGAGE PHYSICS DPP
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise subjective type|51 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT & CIRCUITS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Kirchhoff s law and simple circuits|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-COULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD-Exercises
- In fig. a plastic rod in the form of circular are with charge +Q unfor...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows that E has the same value for all points is front fo an i...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the tracks of three charged particles in a unform electro...
Text Solution
|
- Three small spheres x,y, and z carry charges of equal magnitudes and w...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical positive charges are fixed on the y-axis, at equal dista...
Text Solution
|
- An electric field is defined in terms of q(0) a small positive charge....
Text Solution
|
- Three identical positive charges Q are arranged at the vertices of an...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges of +5xx10^(-19)C and +20xx10^(-19)C are separated by...
Text Solution
|
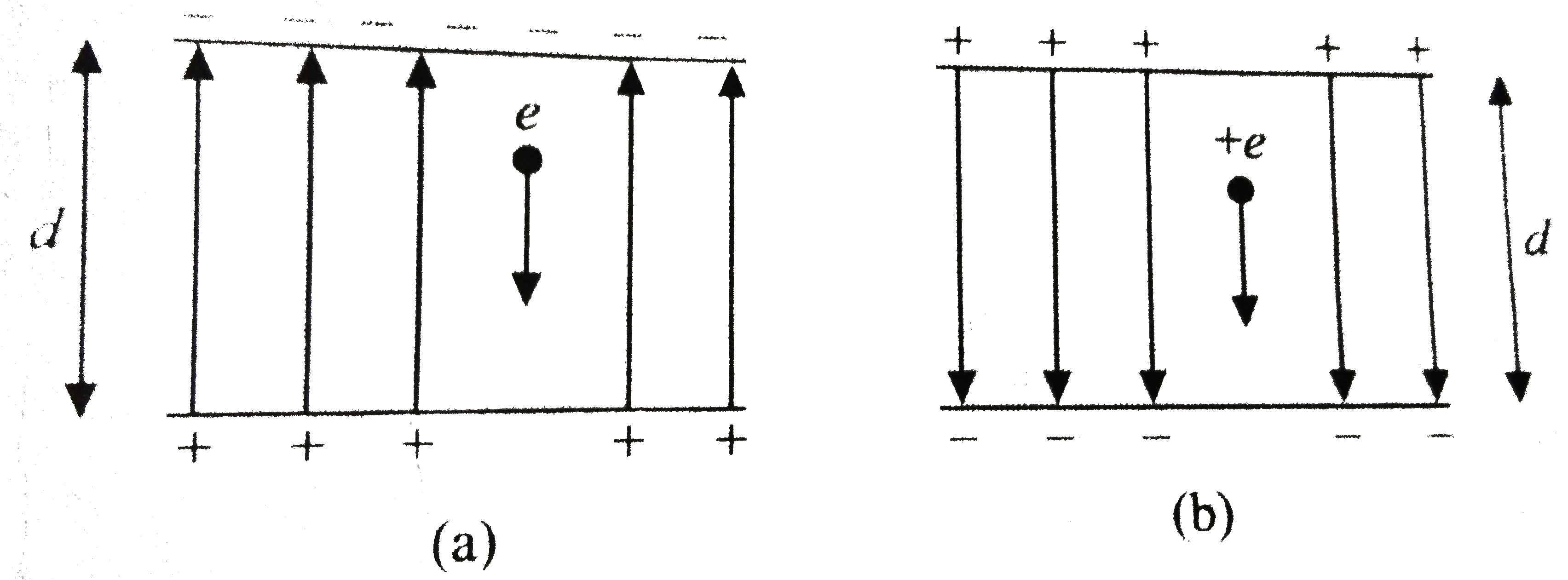
- An electron (mass m(e ))falls through a distance d in a uniform electr...
Text Solution
|
- Two charged metal plates in vacuum are 10cm apart. A uniform electric ...
Text Solution
|
- Two idential point charges Q are kept at a distance r from each other....
Text Solution
|
- Two point electric charges of unknown magnitudes and signs are placed ...
Text Solution
|
- Two pieces of plasitic a full ring and a half ring, have the same radi...
Text Solution
|
- A droplet of ink in an industrial ink-jet printer carries a charge of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles A and B having charges 8.0 xx 10 ^(-6) C and -2.0 xx 1...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charge +-q are placed on the axis at x= -a and x= +a, as sho...
Text Solution
|
- Two point-like charge a and b whose strengths are equal in absolute va...
Text Solution
|
- An electron moving in a gravitational free space enters a unifrom elec...
Text Solution
|
- Protons are projected with an initial speed v(i)=6kms^(-1) from a file...
Text Solution
|
- Two indentical point charges having magnitude q each are placed as sho...
Text Solution
|
 ,
,