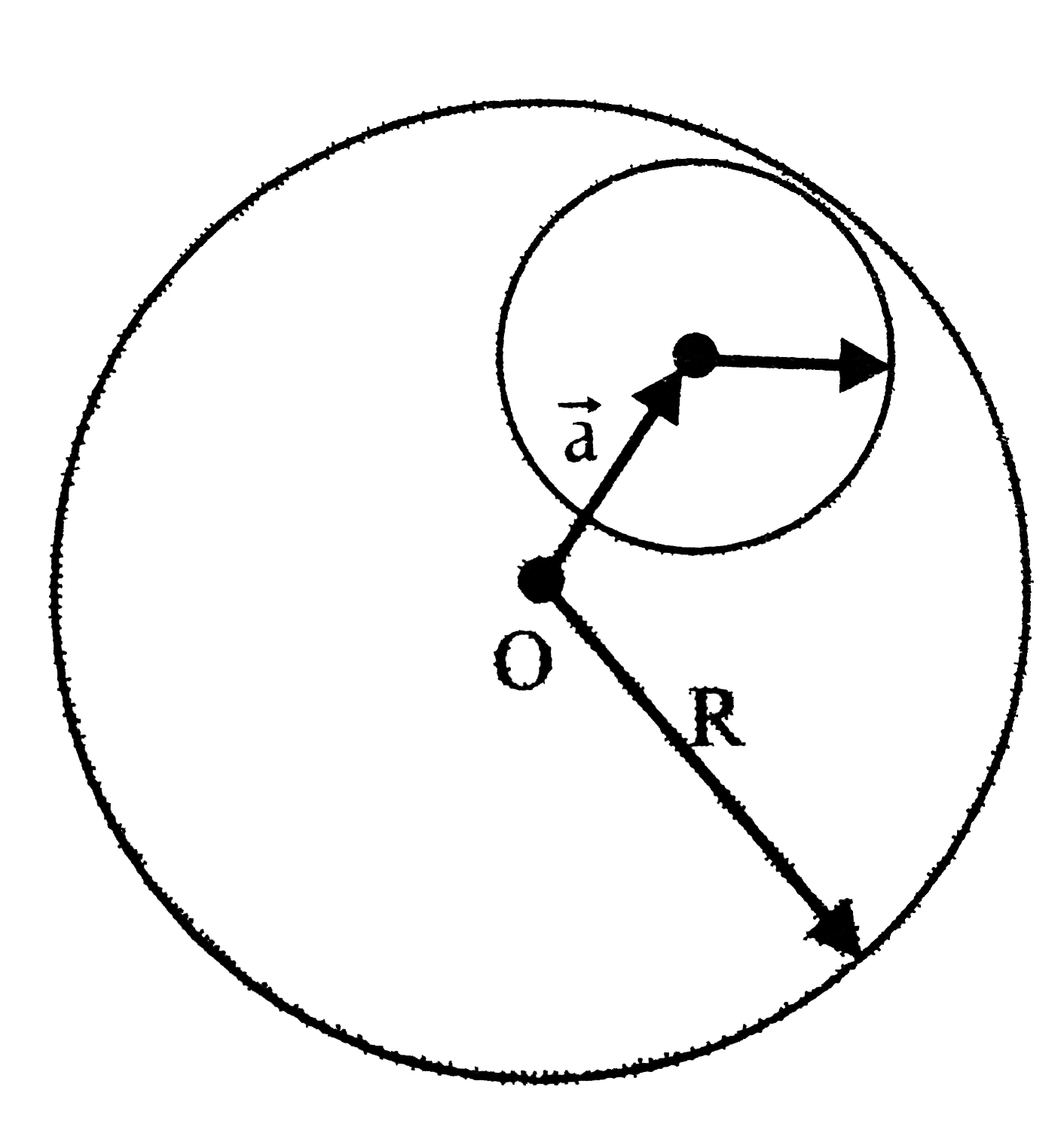
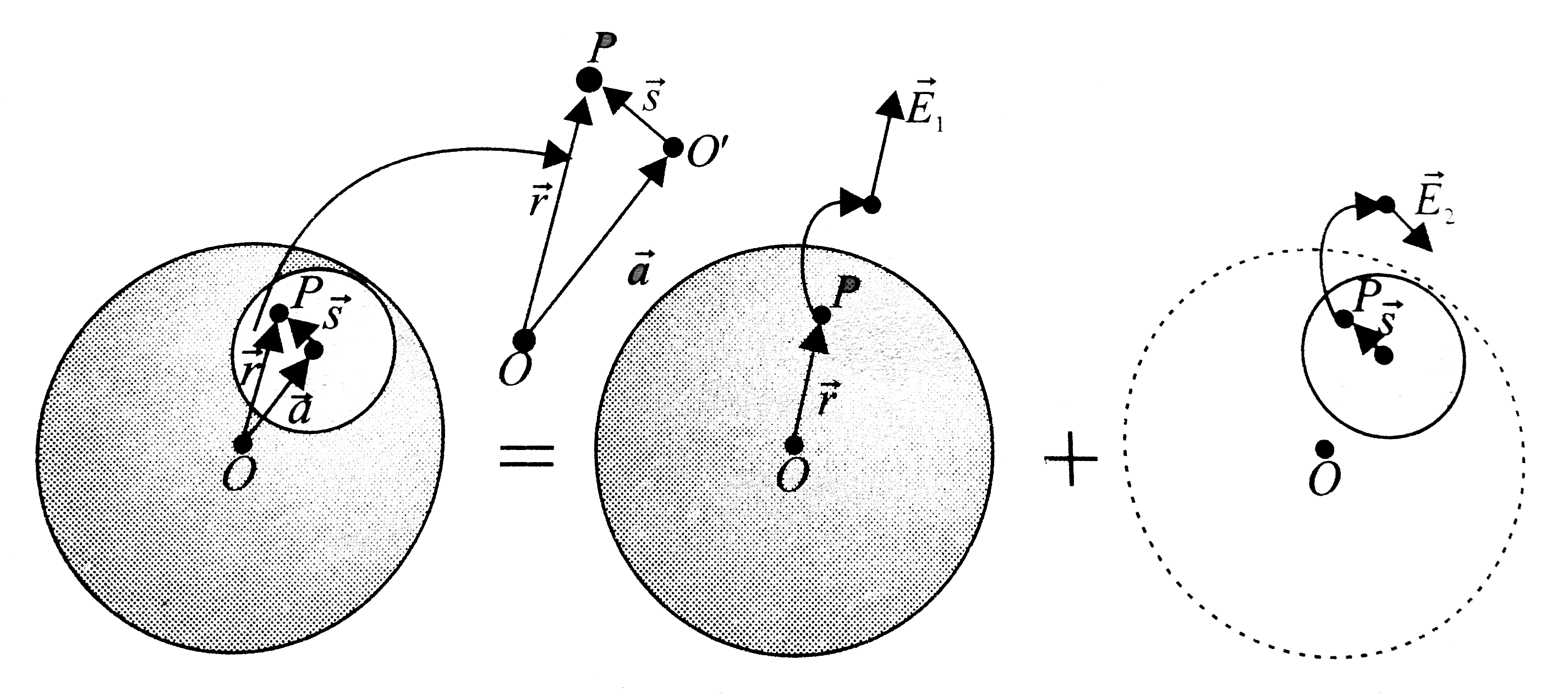
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 2.1|16 VideosELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 2.2|14 VideosELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise MCQ s|38 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT AND CIRCUIT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Interger|8 VideosELECTRIC POTENTIAL
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise DPP 3.5|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-ELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW-Example
- The electric field in a cubical volume is vecE = E0 (1+z/a) hati + E...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge q is placed on the top of a cone of semi vertex angle t...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of radius R has a uniform volume density rho. A spherical cav...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth chute is made in a dielectric sphere of radius R and uniform ...
Text Solution
|
- An infinitely large layer of charge of uniform thickness t is placed n...
Text Solution
|
- There are n large parallel plate conductors carrying charge Q1,Q2,………....
Text Solution
|
- Find the electrostatic force of interaction between two halves of a sp...
Text Solution
|