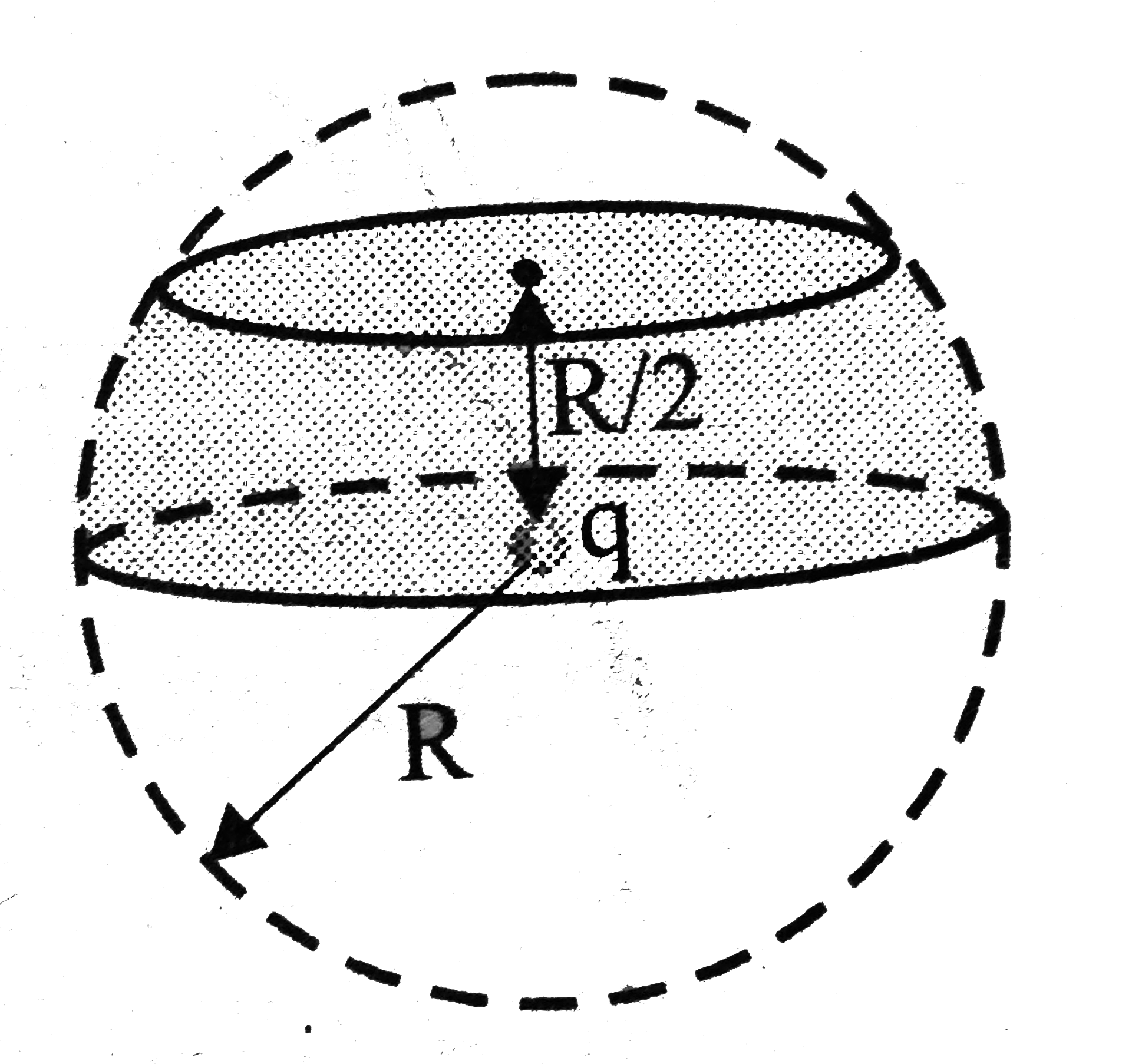
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|8 VideosELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehension|36 VideosELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|12 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT AND CIRCUIT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Interger|8 VideosELECTRIC POTENTIAL
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise DPP 3.5|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-ELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW-Single Correct
- The electric field vecE1 at one face of a parallelopiped is uniform ov...
Text Solution
|
- A dielectric in the form of a sphere is introduced into a homogeneous ...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field on two sides of a thin sheet of charge is shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of radius R carries charge such that its volume charge densit...
Text Solution
|
- An uncharged conducting large plate is placed as shown. Now an electri...
Text Solution
|
- An uncharge aluminium block has a cavity within it. The block is place...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a uniformly charged hemisphere of radius R. It has a volu...
Text Solution
|
- Consider an infinite line charge having uniform linear charge density ...
Text Solution
|
- One-fourth of a sphere of radius R is removed as shown in figure. An e...
Text Solution
|
- A nonconducting sphere of radius R is filled with uniform volume charg...
Text Solution
|
- A large charged metal sheet is placed in a uniform electric field, per...
Text Solution
|
- A positively charge sphere of radius r0 carries a volume charge densit...
Text Solution
|
- Four very large metal plates are given charges as shown in figure. The...
Text Solution
|
- A conic surface is placed in a uniform electric field E as shown in fi...
Text Solution
|
- Flux passing through the shaded surface of a sphere when a point charg...
Text Solution
|
- An infinitely long line charge having a uniform charge per unit length...
Text Solution
|
- Two infinite sheets having charge densities sigma1 and sigma2 are plac...
Text Solution
|
- Two nonconducting infinite planes sheets having charges Q and 2Q are p...
Text Solution
|
- Three large identical conducting parallel plates carrying charge +Q , ...
Text Solution
|
- The number of electric field lines crossing an area DeltaS is n1 when ...
Text Solution
|