Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CAPACITOR AND CAPACITANCE
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Examples|10 VideosCAPACITOR AND CAPACITANCE
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 4.1|13 VideosATOMIC PHYSICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise ddp.4.3|15 VideosCENGAGE PHYSICS DPP
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise subjective type|51 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-CAPACITOR AND CAPACITANCE-Integer
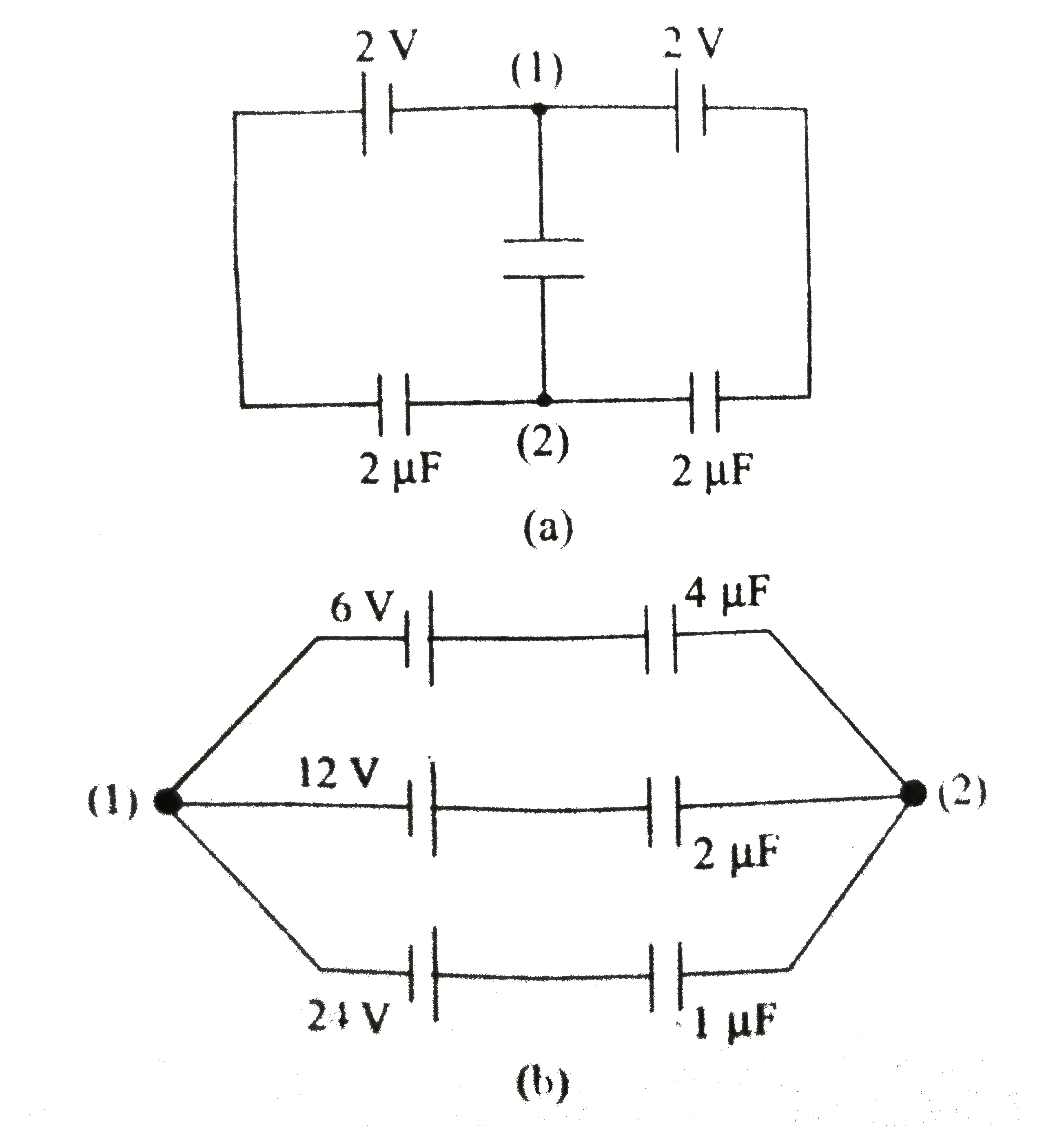
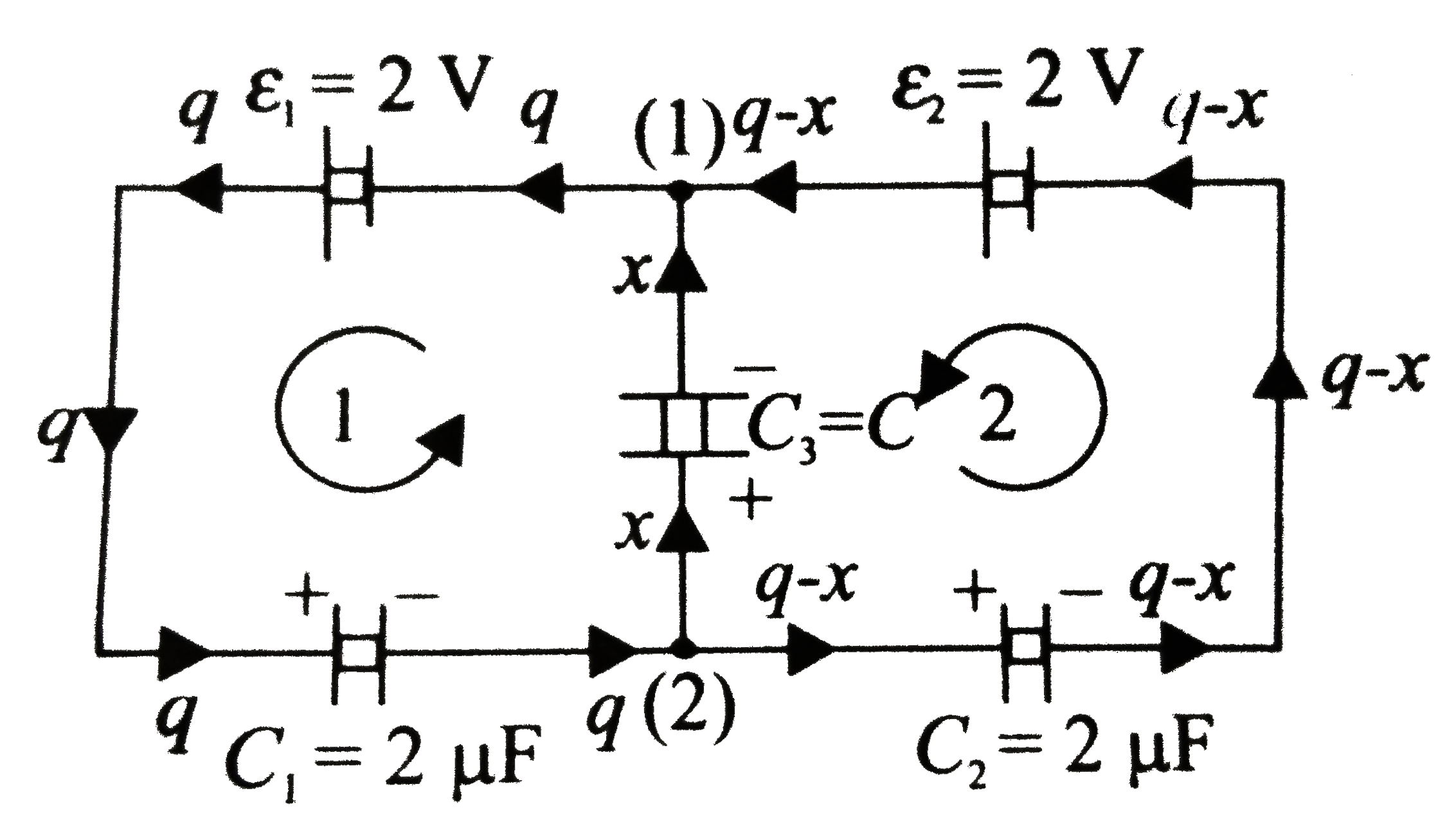
- Find the potential difference V(a)-V(b) between the points (1) and (2)...
Text Solution
|
- Each capacitance shown in is in muF. Find the charge on 6 muF. .
Text Solution
|
- In, a potential of +12 V is given to point A, and point B is earthed. ...
Text Solution
|
- Capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor becomes 4/3 times its origin...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical drop of capacitance 12 muF is broken into eight drops of e...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel plate capacitor of capacity C(0) is charged to a potential ...
Text Solution
|