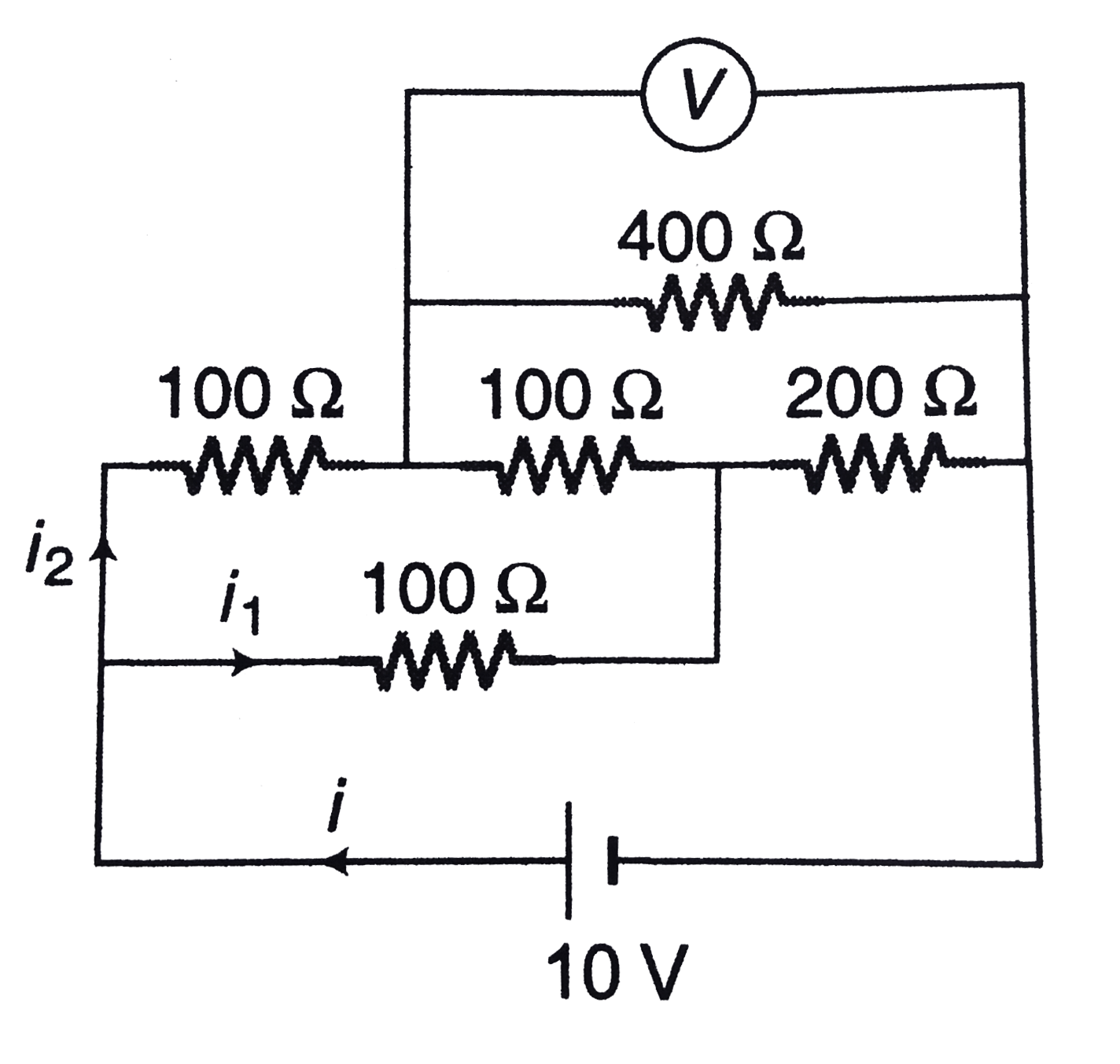
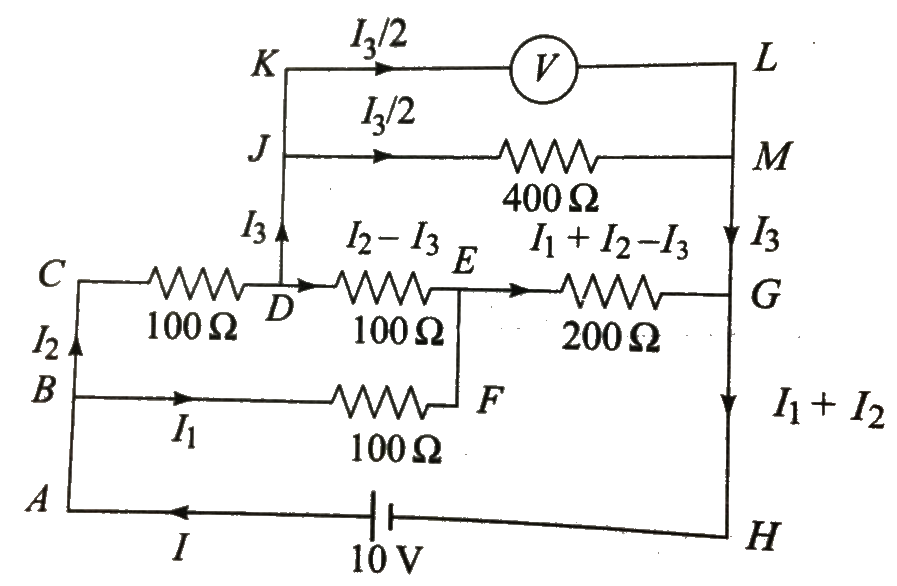
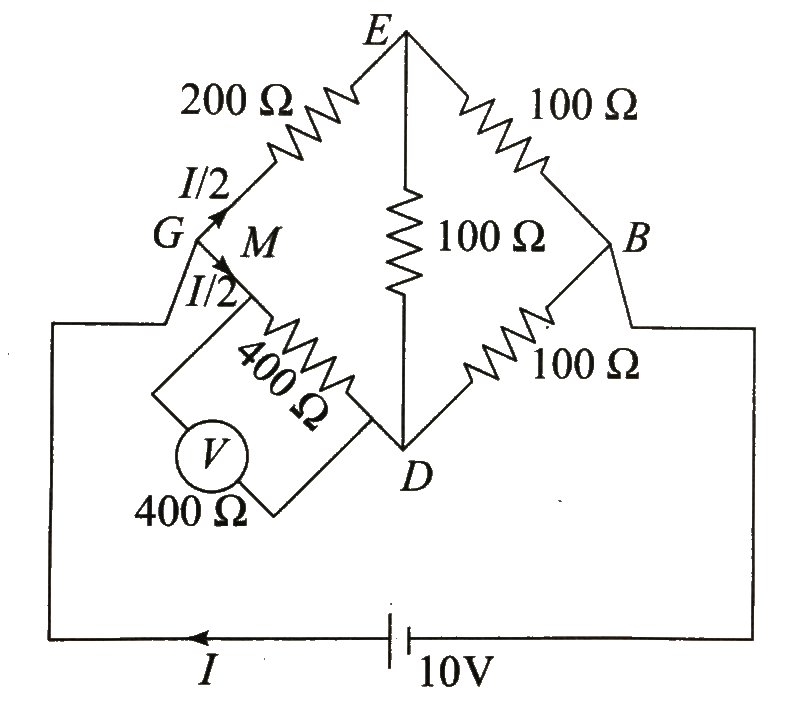
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRICAL MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 6.1|15 VideosELECTRICAL MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|18 VideosELECTRICAL MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise M.C.Q|2 VideosELECTRIC POTENTIAL
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise DPP 3.5|15 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise compression type|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-ELECTRICAL MEASURING INSTRUMENTS-Solved Examples
- A galvanometer of resistance 95 Omega, shunted resistance of 5 Omega, ...
Text Solution
|
- An electrical circuit is shown in figure. Calculate the potential diff...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform wire AB of length 1 m, an unknown resistance X and a re...
Text Solution
|
- An unknown resistance X is to be determined using resistances R1, R2 o...
Text Solution
|