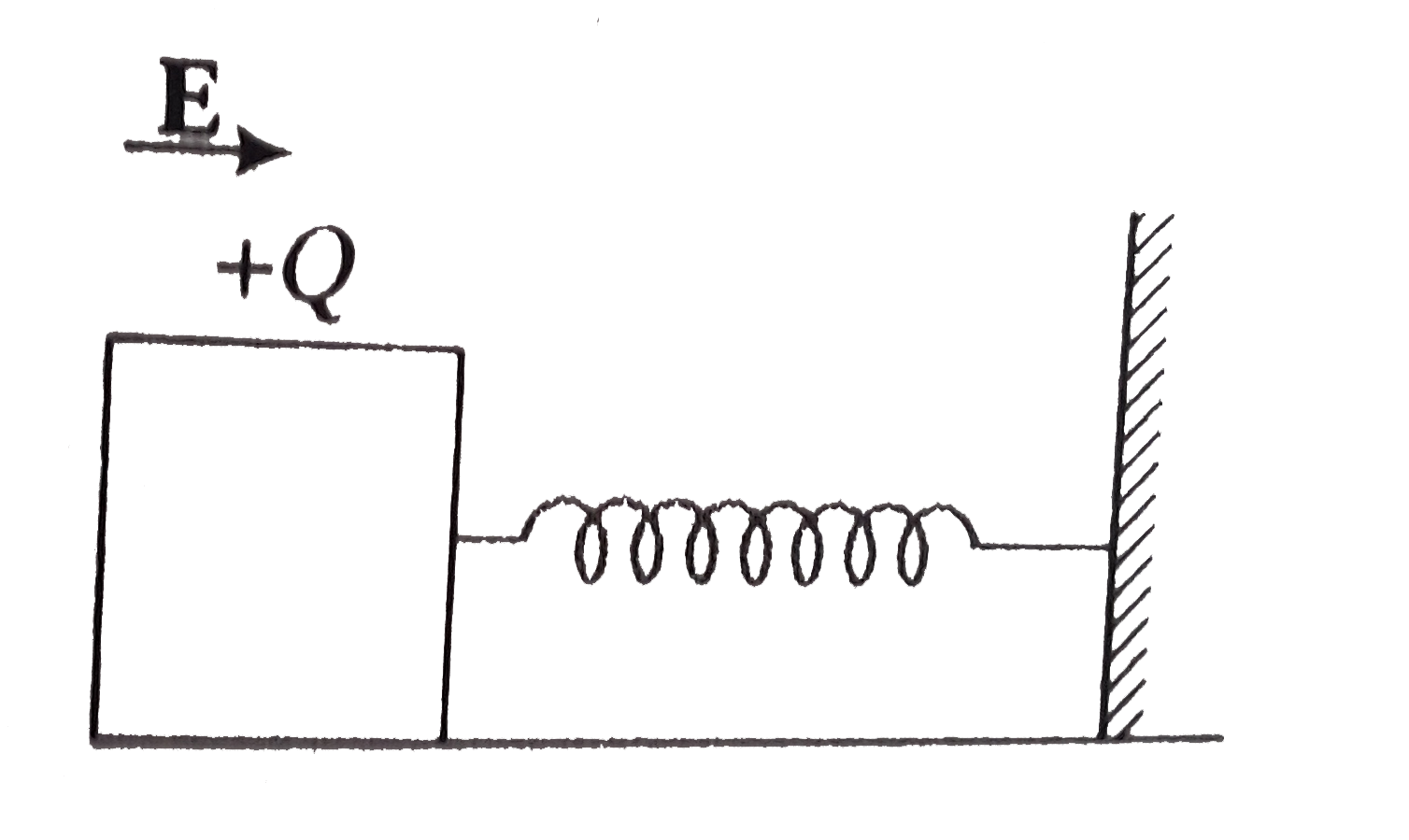
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion and Reason Type|8 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehension Type|94 VideosMAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct Answer type|2 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 5
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3-True and False
- A wooden block performs SHM on a frictionless surface with frequency v...
Text Solution
|
- In an electrolytic solution the electric current is mainly due to the ...
Text Solution
|
- Electrons in a conductor have no motion in the absence of a potential ...
Text Solution
|
- The current - voltage graphs for a given metallic wire at two differen...
Text Solution
|