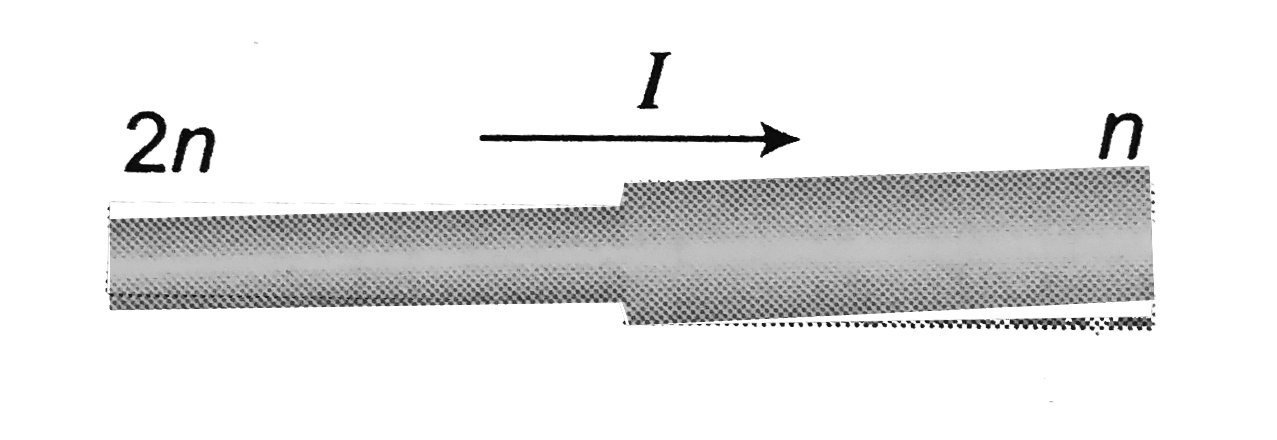
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two cylindrical rods of uniform cross-section area A and 2A, having fr...
Text Solution
|
- Two cylindrical rods of uniform cross-section area A and 2A , having f...
Text Solution
|
- Current I is flowing through a copper wire of radius r with drift velo...
Text Solution
|
- The current i flows in a wire of circular cross-section with the free ...
Text Solution
|
- The drift velocity of free electrons in a conductor is v, when a curre...
Text Solution
|
- If A is the area of cross section of conductor, e be the charge on the...
Text Solution
|
- If A is the area of cross section of conductor, v(d) is the drift velo...
Text Solution
|
- If n,e,A and v(d) are free electron density inside conductor , charge ...
Text Solution
|
- When a current of 1 A flows through a copper wire of cross sectional a...
Text Solution
|