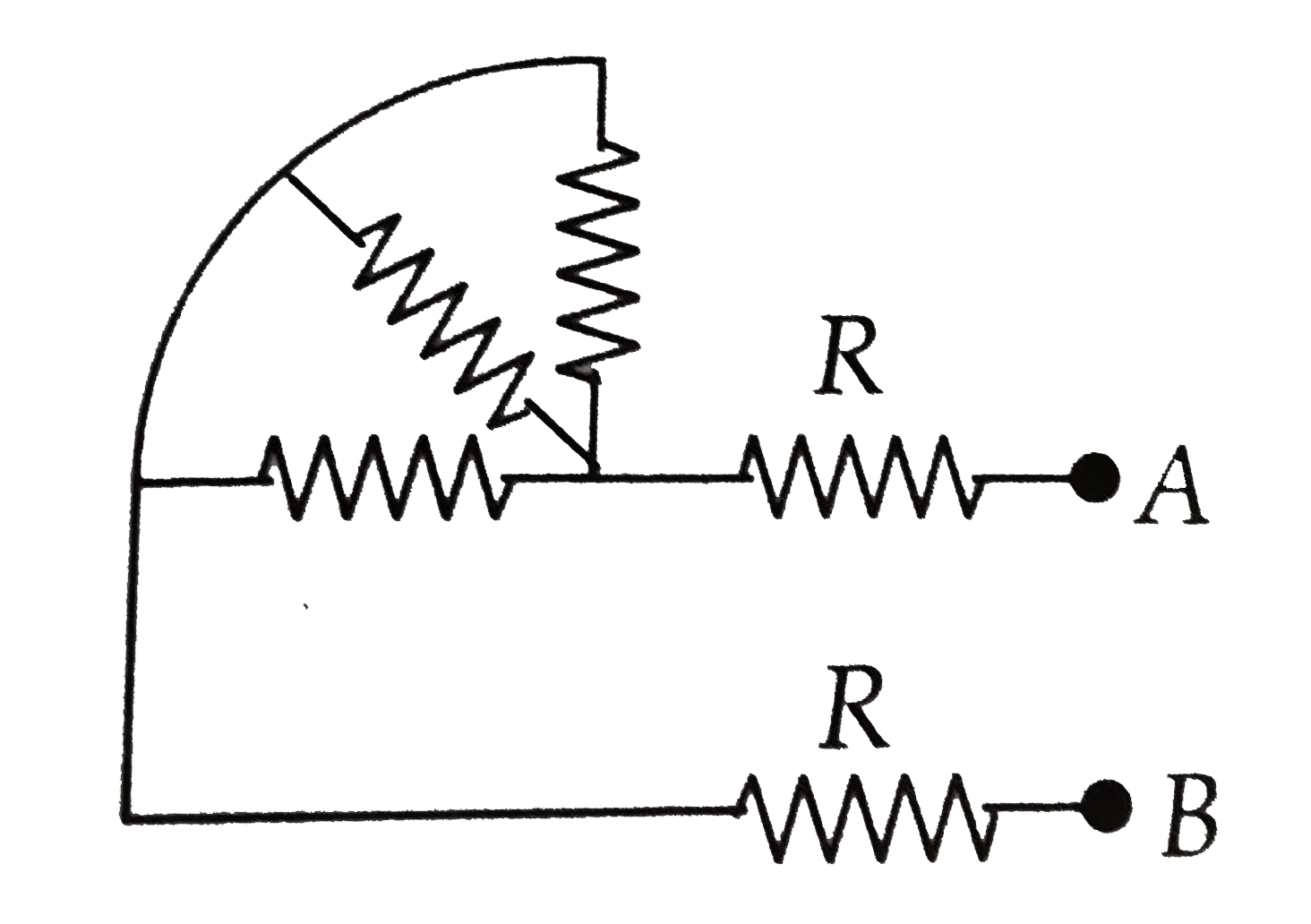
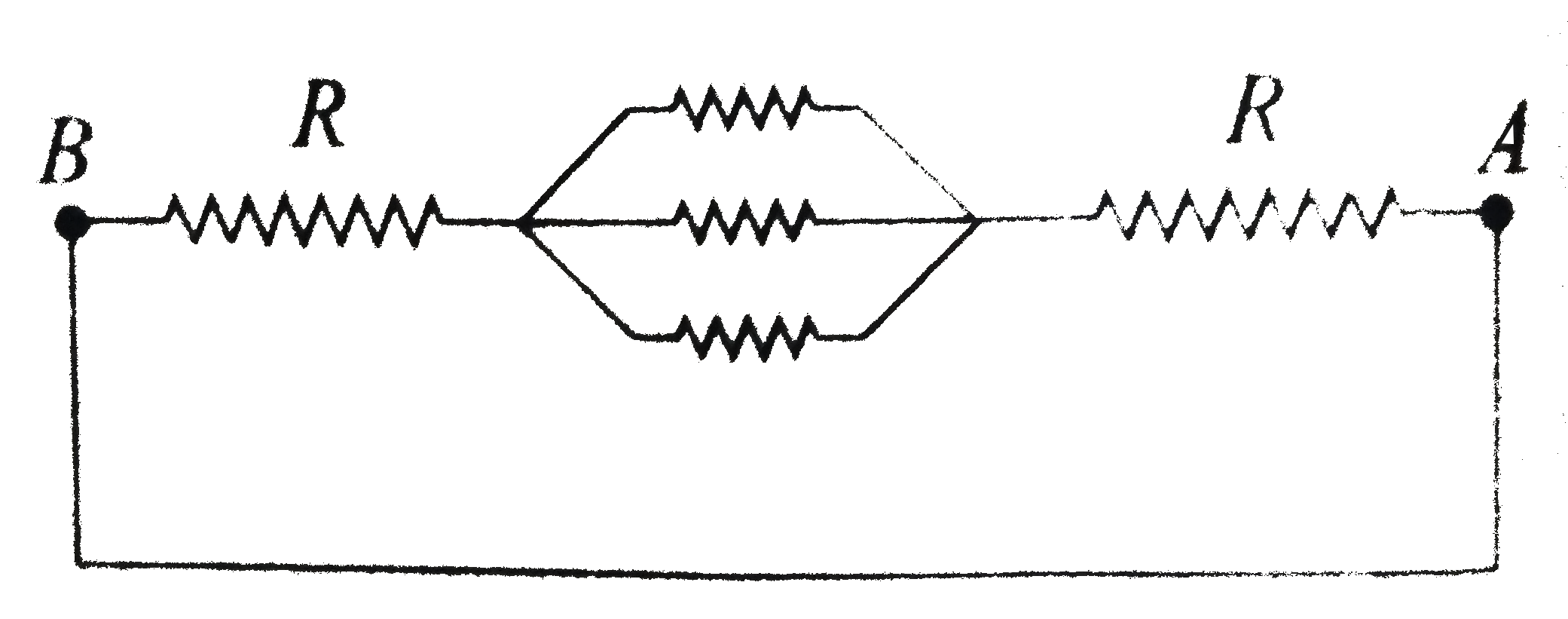
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The potential difference between A and B is V. The values of some resi...
Text Solution
|
- If the value of resistance is 10.845 Omega and the value of current is...
Text Solution
|
- The resistance of a metal is given by R = V//I , where V is potential ...
Text Solution
|
- The current enters at A and leaves at F. The values of some resistance...
Text Solution
|
- The potential difference between A and B is V. The values of some resi...
Text Solution
|
- In a circuit potential difference across resistence V = (4 +- 0.25)V a...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the value of the resistance R in the circuit in the so that ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the value of the resistance R in the circuit shown in the fi...
Text Solution
|
- An unknown resistance is connected in parallel with a 15Omega resistan...
Text Solution
|