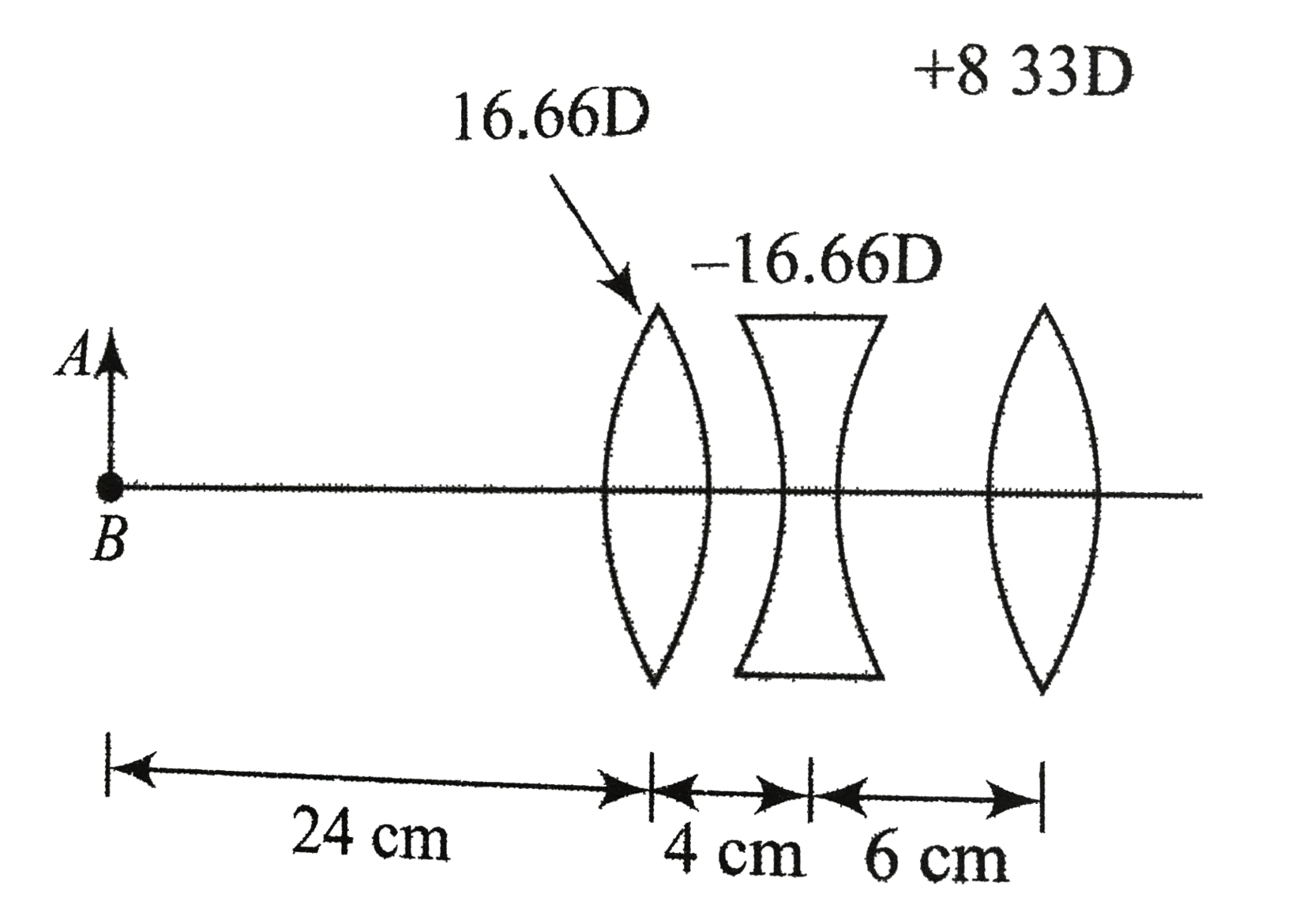Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Examples|15 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise1.1|14 VideosELECTRON,PHONTS,PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT & X-RAYS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 3.3|15 VideosHEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Thermal Power in Resistance Connected in Circuit|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Integer Type
- In Figure. , the length of object AB is 9cm. Find the nature and posit...
Text Solution
|
- The focal length of a thin biconvex lens is 20cm. When an object is mo...
Text Solution
|
- A large glass slab (mu=5//3) of thickness 8cm is placed over a point s...
Text Solution
|
- Image of an object approaching a convex mirror of radius of curvature ...
Text Solution
|
- Water (with refractive index =4//3) in a tank is 18cm deep. Oil of ref...
Text Solution
|