Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise1.1|14 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise1.2|20 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer Type|4 VideosELECTRON,PHONTS,PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT & X-RAYS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 3.3|15 VideosHEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Thermal Power in Resistance Connected in Circuit|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Solved Examples
- A telescope has a objective of focal length 50 cm and an eye-piece of ...
Text Solution
|
- A plano-convex lens has thickness 4cm. When places on a horizontal tab...
Text Solution
|
- (a) A short linear object of length b lies along the axis of a concave...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel bean of light travelling in water (refractive index = 4/3) ...
Text Solution
|
- An image Y is formed of a point object x by a lens whose optic axis is...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travelling in air is incident at grazing angle (incide...
Text Solution
|
- A right angles prism (45^(@),90^(@), 45^(@)) of refractive index n ha...
Text Solution
|
- A thin plano-convex lens of focal length f is split into two halves. O...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length 15cm and a concave mirror of focal lengt...
Text Solution
|
- A thin equiconvex lens of refractive index 3//2 is placed on a horizon...
Text Solution
|
- The refractive indices of the crown glass for violet and red lights ar...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows an irregular block of material of refractive indec sqrt(2...
Text Solution
|
- An object is approaching a convex lens of focal length 0.3m with a spe...
Text Solution
|
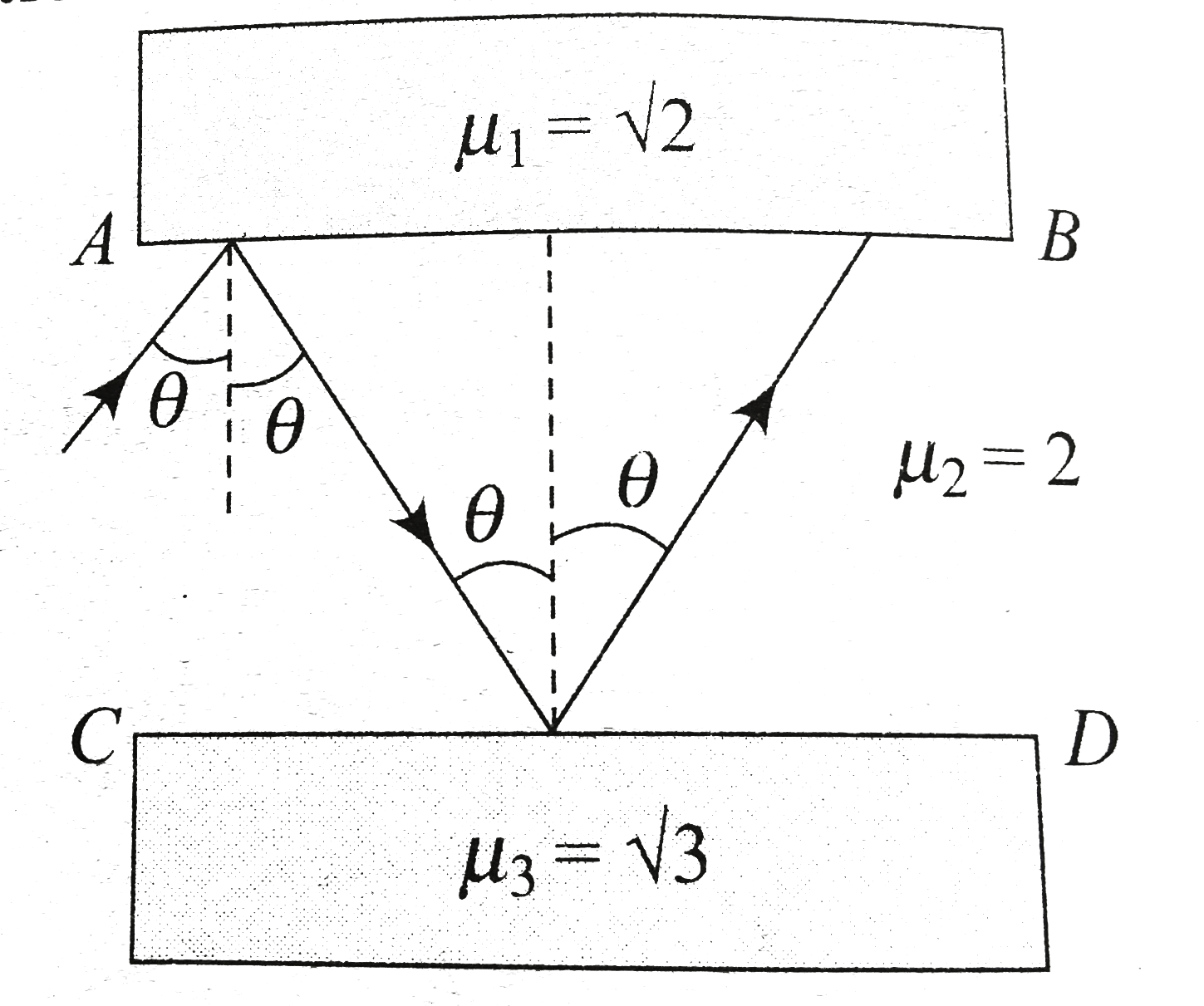
- AB and CD are surfaces ot two slabs as shown in Figure . The medium be...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light strikes a plane mirror at an angle of incidence 45^@ as...
Text Solution
|