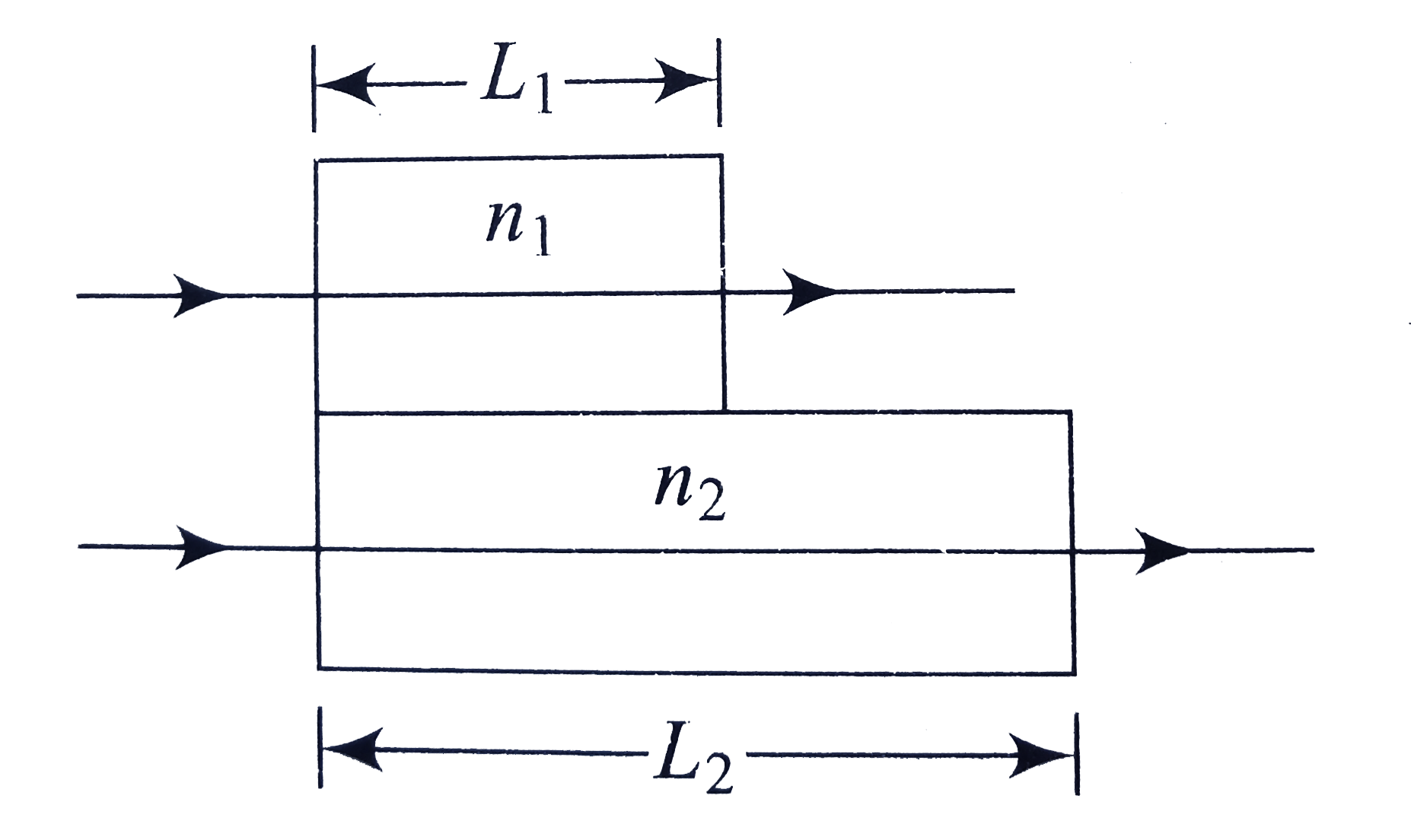
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
WAVE OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|8 VideosWAVE OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion- Reasoning|13 VideosWAVE OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|11 VideosSOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise single correct Ansewer type|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-WAVE OPTICS-Single Correct
- In Young's double-slit experiment, the slit are 0.5 mm apart and the i...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows two coherent sources S(1) and S(2) emitting wavelength la...
Text Solution
|
- Two waves of light in air have the same wavelength and are intially in...
Text Solution
|
- Light from a sources emitting two wavelengths lambda(1) and lambda(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- The wavefront of a light beam is given by the equation x + 2y + 3x = c...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in figure waves with identical wavelengths and amplitudes and...
Text Solution
|
- If the distance between the first maxima and fifth minima of a double-...
Text Solution
|
- In YDSE, D = 1 m, d = 1 mm, and lambda = 5000 nm. The distance of the...
Text Solution
|
- Let S(1) and S(2) be the two slits in Young's double-slit experiment. ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows two coherent sources S(1)-S(2) vibrating in same phase. A...
Text Solution
|
- The path difference between two interfering waves at a point on the sc...
Text Solution
|
- In YDSE shown in figure a parallel beam of light is incident on the sl...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, if a parallel beam of light is incident on the pl...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, a parallel beam of light is incident on the plane...
Text Solution
|
- Interference fringes were produced using light in a doulbe-slit experi...
Text Solution
|
- Two coherent ligh sources each of wavelength lambda are separated by a...
Text Solution
|
- M(1) and M(2) are plane mirrors and kept parallel to each other. At po...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident on a thin film, As shown in figure, M and N...
Text Solution
|
- If one of the two slits of Young's double-slit experiment is painted s...
Text Solution
|
- Coherent light with wavelength 600nm passes through two very narrow sl...
Text Solution
|