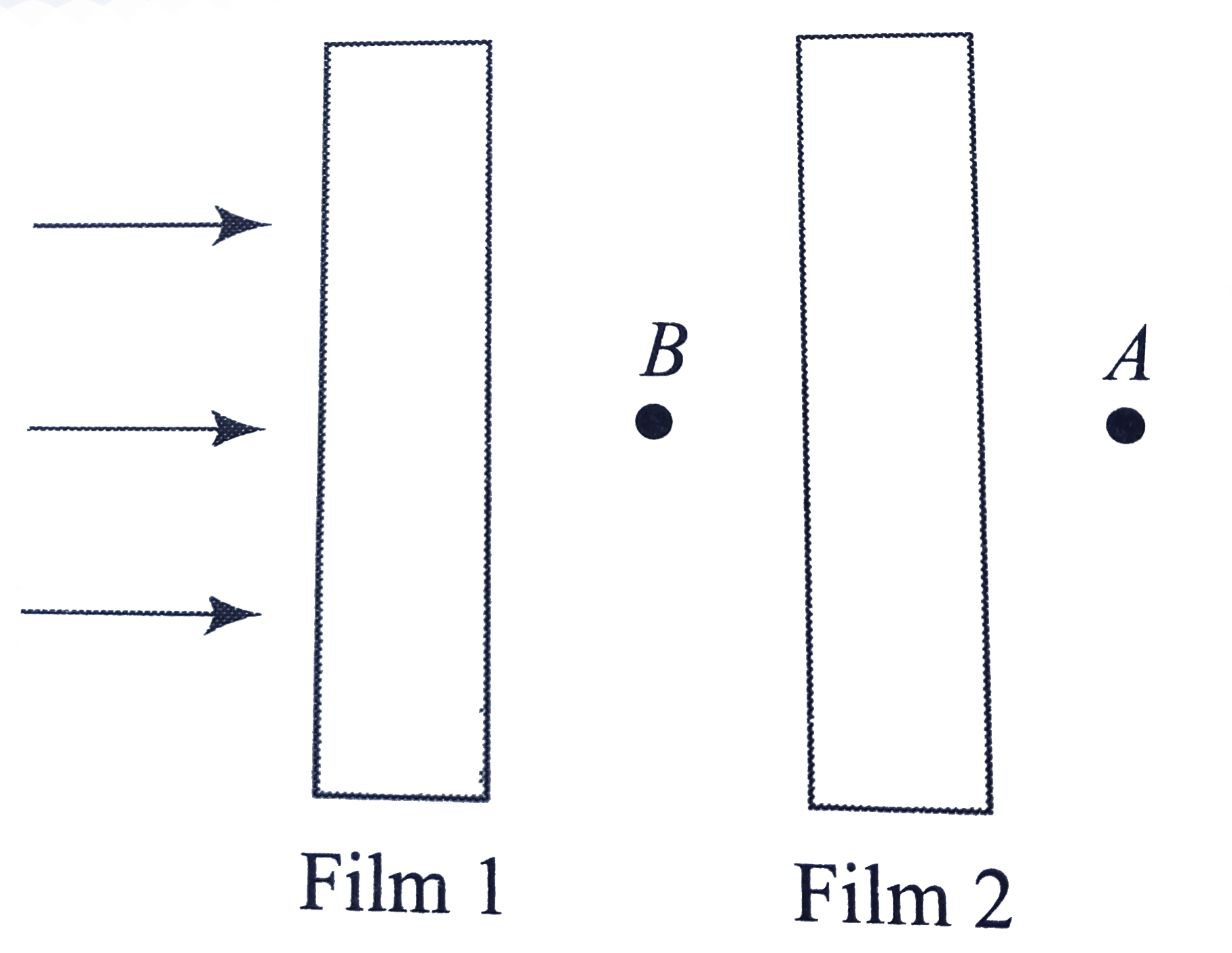
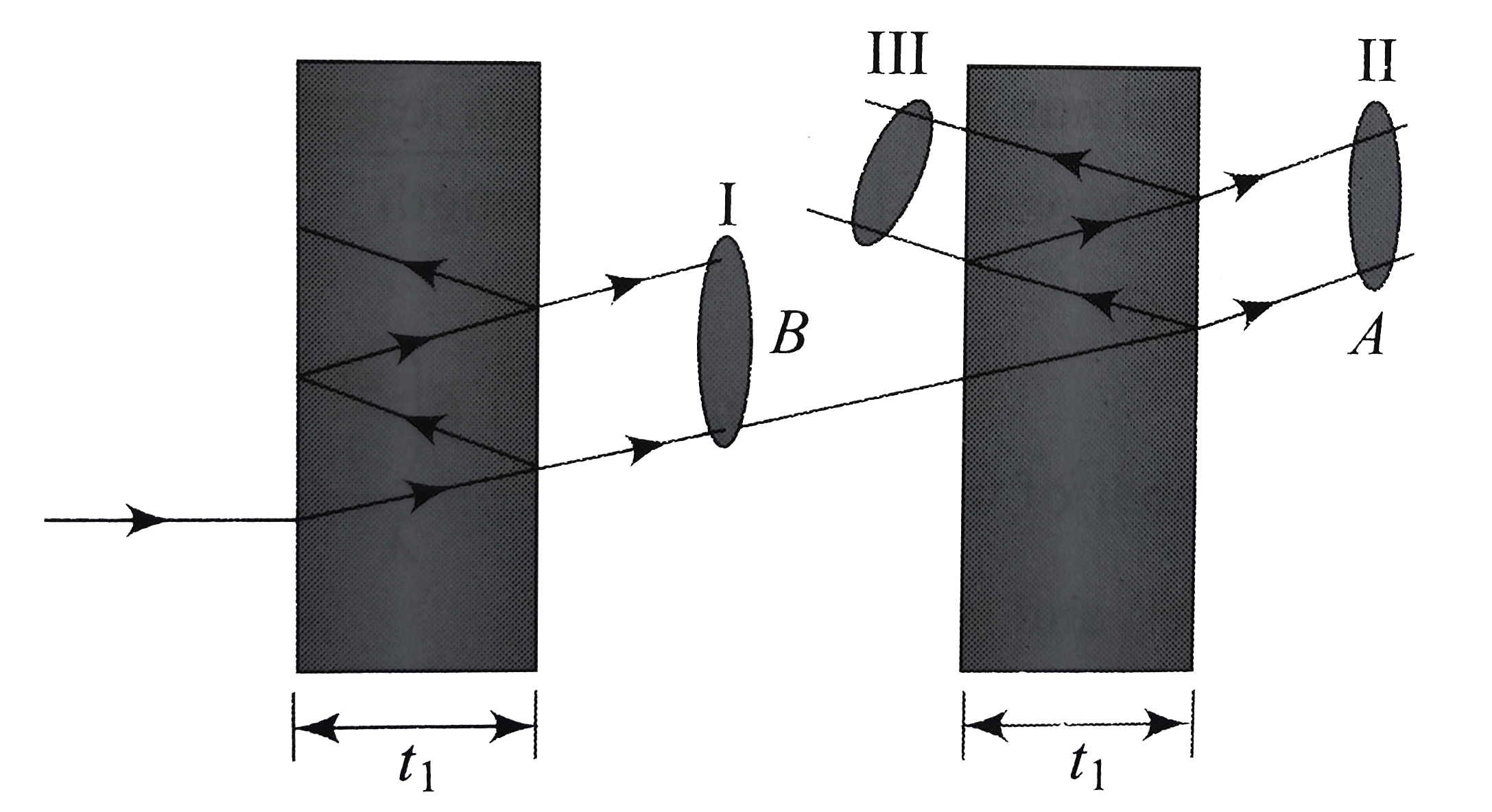
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
WAVE OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|8 VideosWAVE OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion- Reasoning|13 VideosWAVE OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|11 VideosSOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise single correct Ansewer type|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-WAVE OPTICS-Single Correct
- In YDSE, having slits of equal width, let beta be the fringe width and...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical coherent sources of wavelength lambda are placed at (100...
Text Solution
|
- Two thin films of the same material but different thickness are separa...
Text Solution
|
- Consider an YDSE that has different slit width. As a result, amplitude...
Text Solution
|
- In YDSE of equal width slits, if intensity at the center of screen is ...
Text Solution
|
- Two transparent slabs have the same thickness as shown in figure. One ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the speed of light of wavelength lambda =780nm (in air) in a medi...
Text Solution
|
- In young's double-slit experiment, the slit are 2 mm apart and are ill...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's interference experiment, if the slit are of unequal width, ...
Text Solution
|
- Two wavelengths of light lambda(1) and lambda(2) and sent through Youn...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's interference experiment, the central bright fringe can be i...
Text Solution
|
- A flake of glass (refractive index 1.5) is placed over one of the open...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical sources each of intensity I(0) have a separation d = lam...
Text Solution
|
- In a double-slit experiment, instead of taking slits of equal width, o...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's double slit experiment, 12 fringes are observed to be forme...
Text Solution
|
- A certain region of a soap bubble reflects red light of vacuum wavelen...
Text Solution
|
- In a Young's double slit experiment using monochromatic light, the fri...
Text Solution
|
- In the ideal double-slit experiment, when a glass-plate (refractive in...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's double slit experiment, the intensity of light at a point o...
Text Solution
|
- YDSE is carried with two thin sheets of thickness 10.4mu m each and r...
Text Solution
|