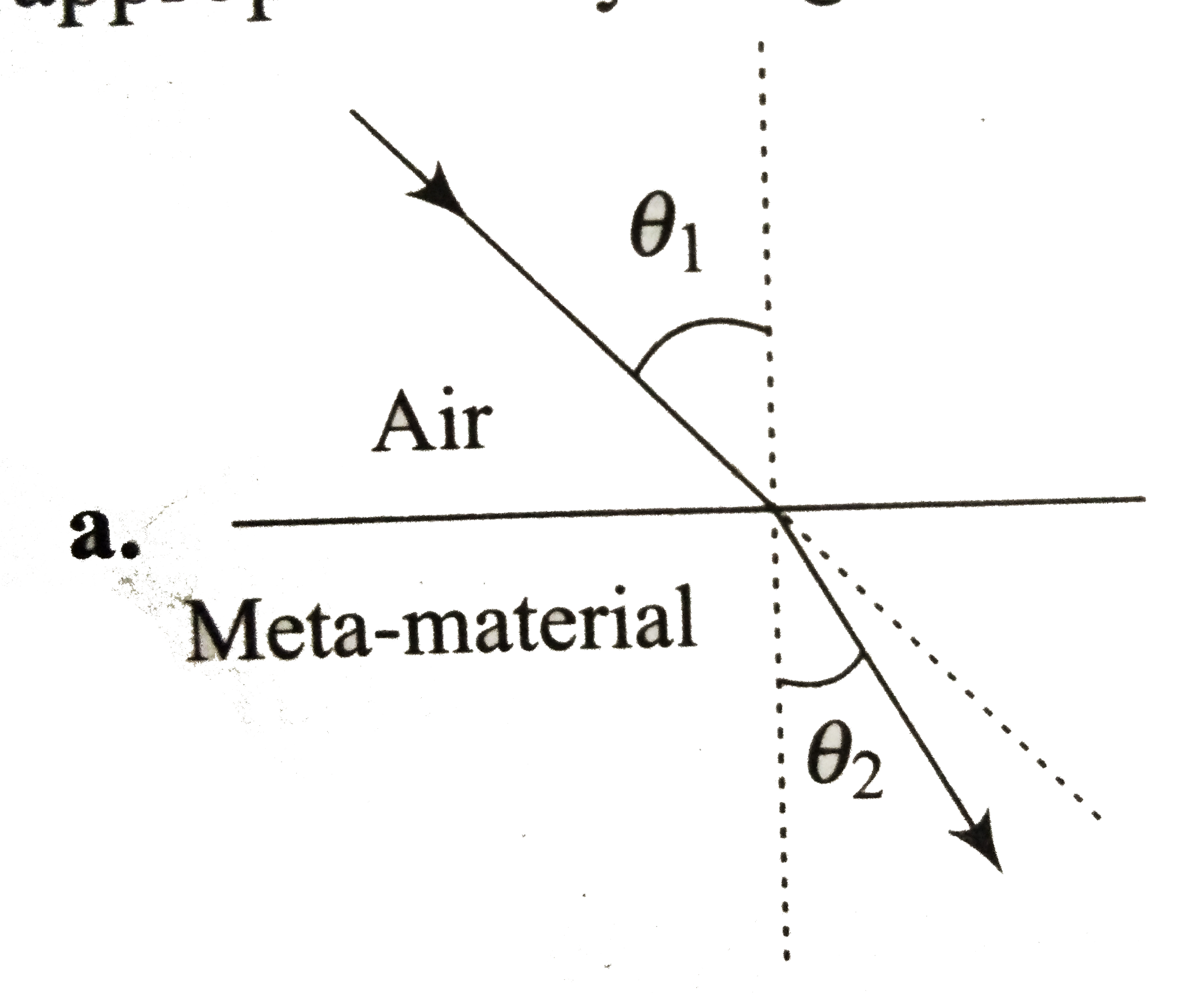
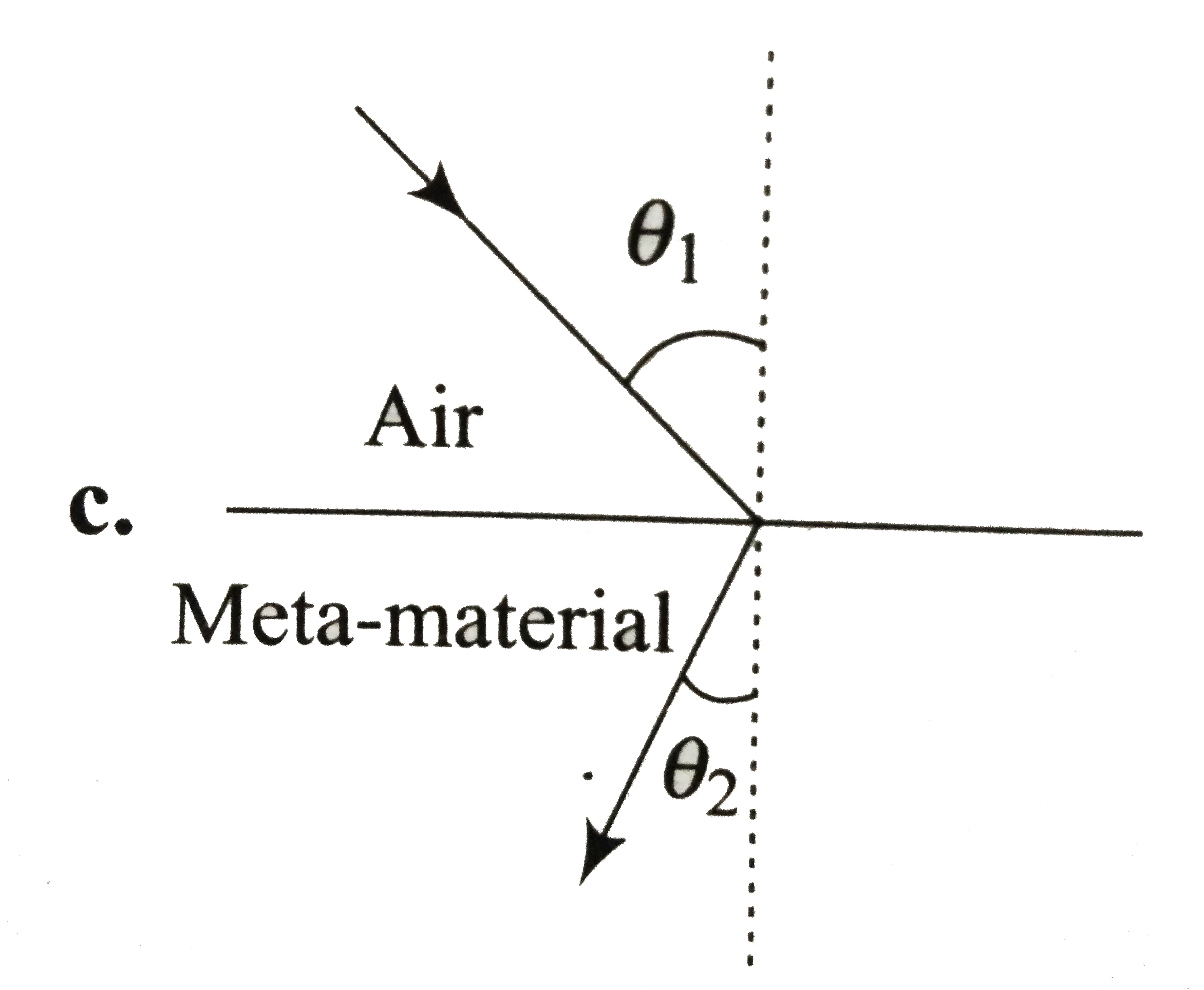
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-WAVE OPTICS-Linked Comprehension type
- Fig. shows a surface XY separating two transparent media, medium 1 and...
Text Solution
|
- Fig. shows a surface XY separating two transparent media, medium 1 and...
Text Solution
|
- Fig. shows a surface XY separating two transparent media, medium 1 and...
Text Solution
|
- Most materials have the refractive index, n gt 1. So, when a light ray...
Text Solution
|
- Most materials have the refractive index, n gt 1. So, when a light ray...
Text Solution
|