Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Single Correct|70 VideosMAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Multiple Correct|25 VideosMAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise1.3|14 VideosINDUCTANCE
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Concept Based|8 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise True and False|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-MAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES-Exercises Subjective
- An alpha-particle is describing a circle of radius 0.45 m in a field o...
Text Solution
|
- In a trapeze-shaped structure, two rigid wires of negligble mass suppo...
Text Solution
|
- A strong magnet is placed under a horizontal conducting ring of radius...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel with 4 spokes is placed with its plane perpendicular to a unif...
Text Solution
|
- A positively charged particle having charge q is accelerated by a pote...
Text Solution
|
- A charged particle +q of mass m is placed at a distanced from another ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting wire of length l is placed on a rough horizontal surface,...
Text Solution
|
- A small circular coil with a mass of m consists of N turns of fine wir...
Text Solution
|
- Two metal strips, each of length, each of length l, are clamped paral...
Text Solution
|
- A metal rod of mass 10 gm and length 25 cm is suspended on two springs...
Text Solution
|
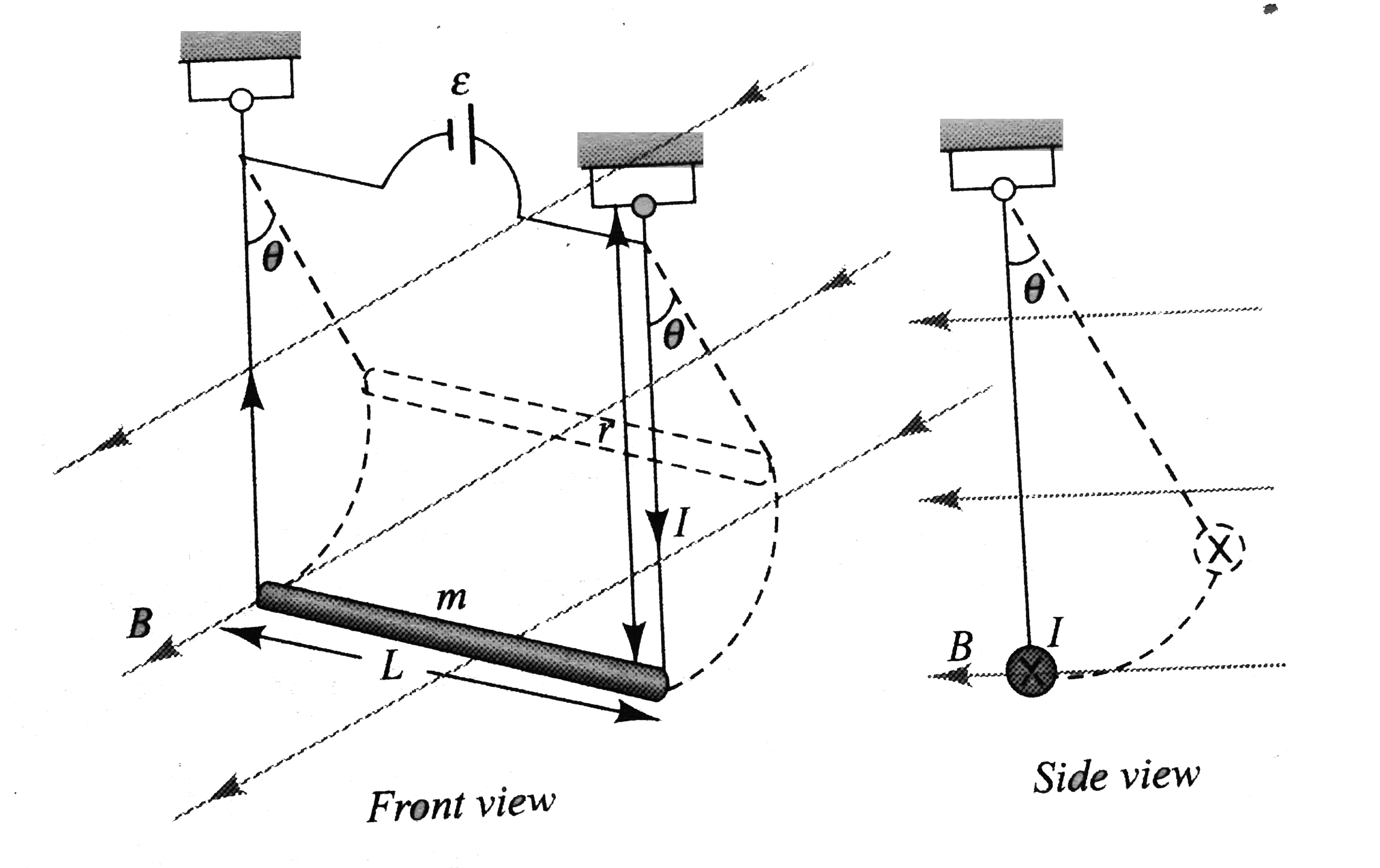


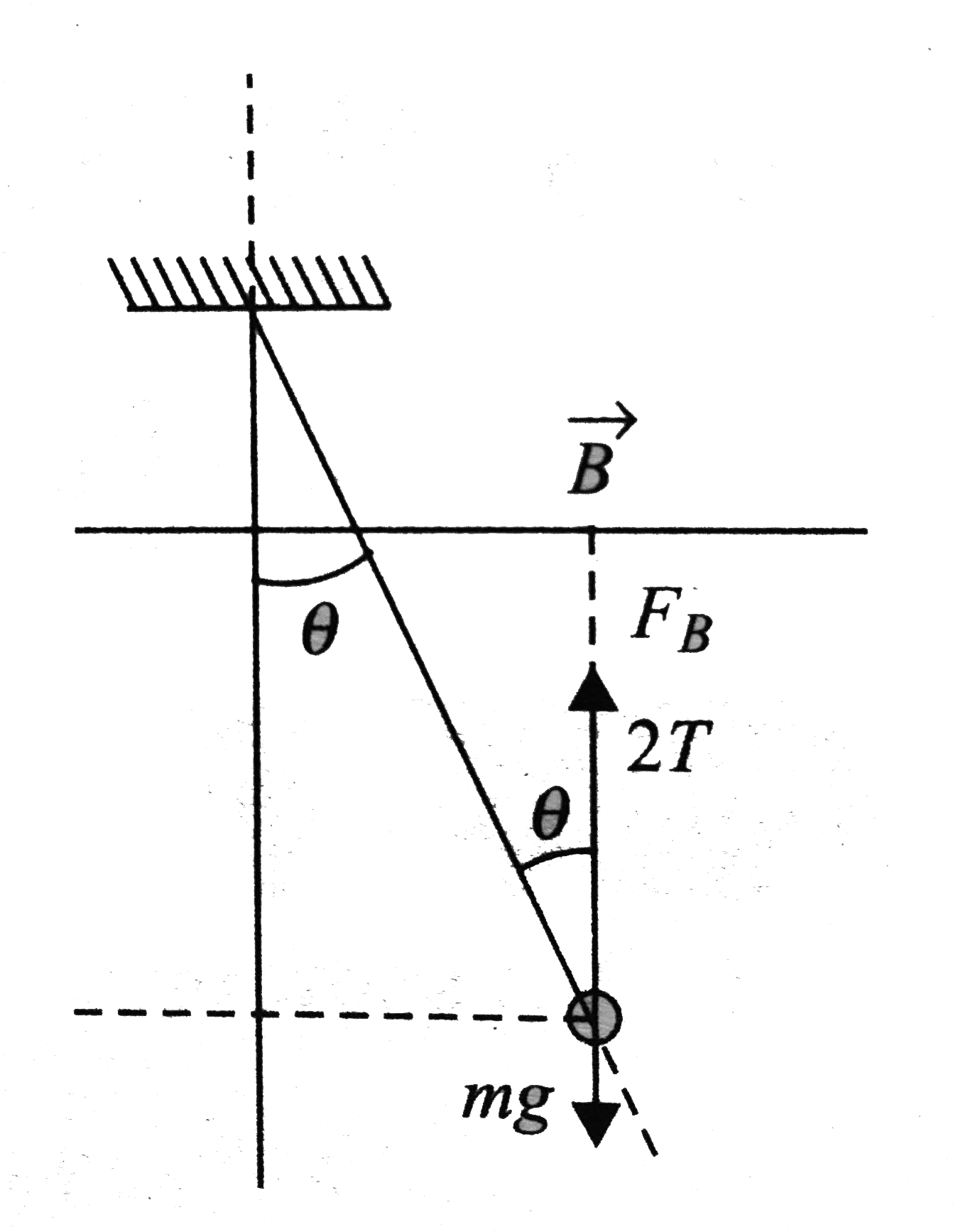
 .
.