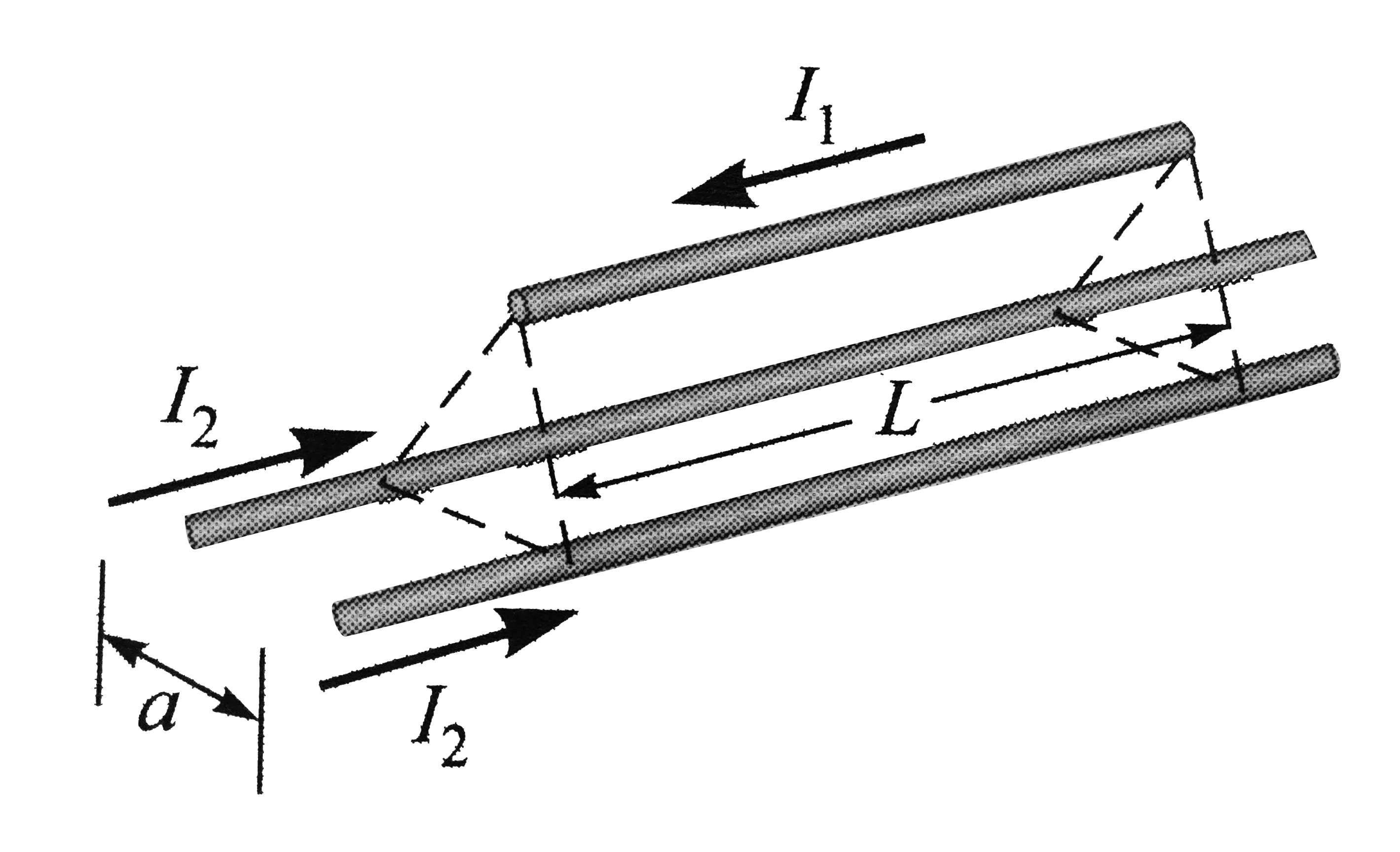
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Example|20 VideosSOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Concept Exercise 2.1|35 VideosRAY OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise DPP 1.6|12 VideosWAVE OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehension Type|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-SOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD-single correct Ansewer type
- Two infinetely long, parallel wires are lying on the ground at distanc...
Text Solution
|
- Three distinct current wires intersect a finite rectangular plane ABCD...
Text Solution
|
- Rank the value of ointvec(B)vec(dl) for the closed paths shown in figu...
Text Solution
|
- Eight wires cut the page perpendicularly at the points shown in figur...
Text Solution
|
- A long thin hollow metallic cylinder of radius R has a current I amper...
Text Solution
|
- A coaxial cable made up of two conductors. The inner conductor is soli...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the cross-sectional view of the hollow cylindrical conduc...
Text Solution
|
- A current I ampere flows along the inner conductor of a co-axial cable...
Text Solution
|
- From a cylinder of radius R, a cyclinder of radius R/2 is removed, as ...
Text Solution
|
- A winding wire which is used to frame a solenoid can bear a maximum 10...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical conductor of radius 'R' carries a current 'i'. The value...
Text Solution
|
- Two coaxil solenoids 1 and 2 of the same length are set so that one is...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical current carrying coaxial hoops, carry current I in an op...
Text Solution
|