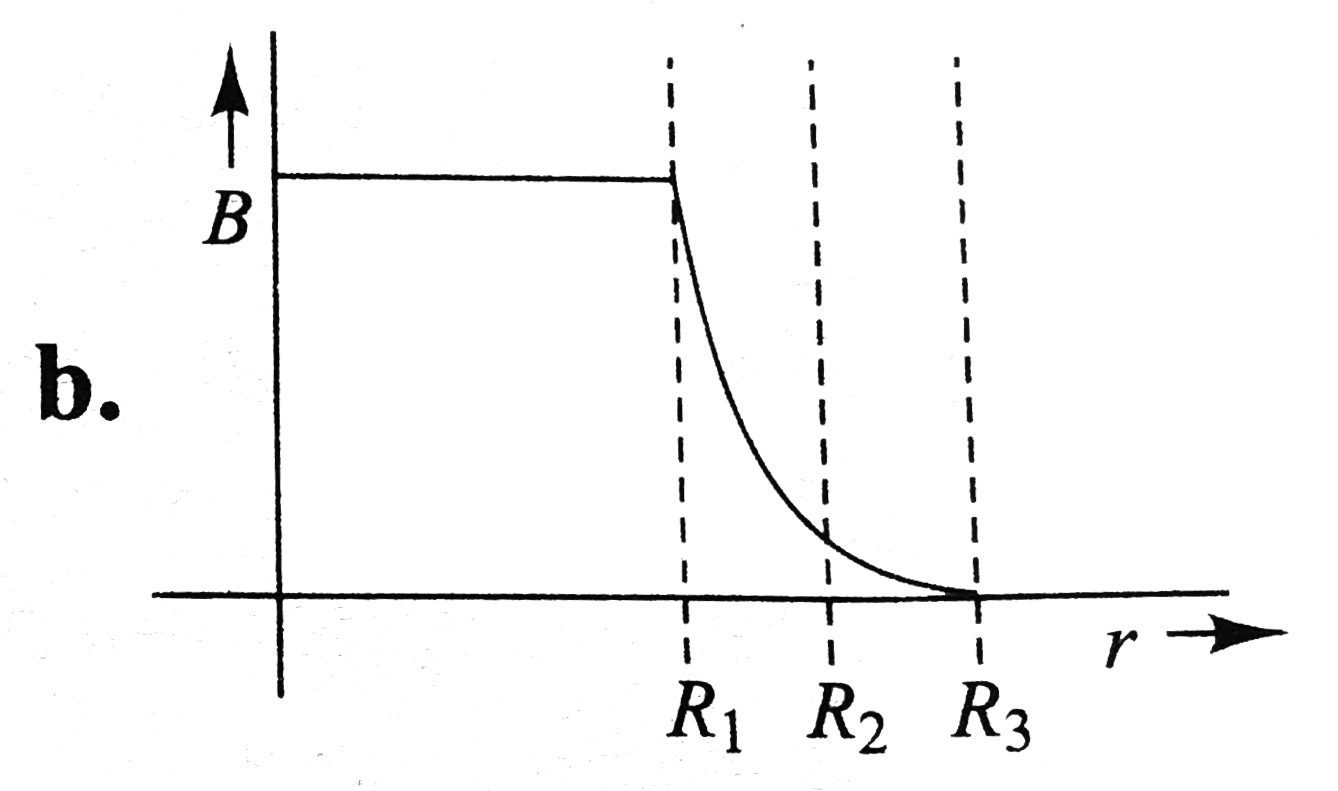
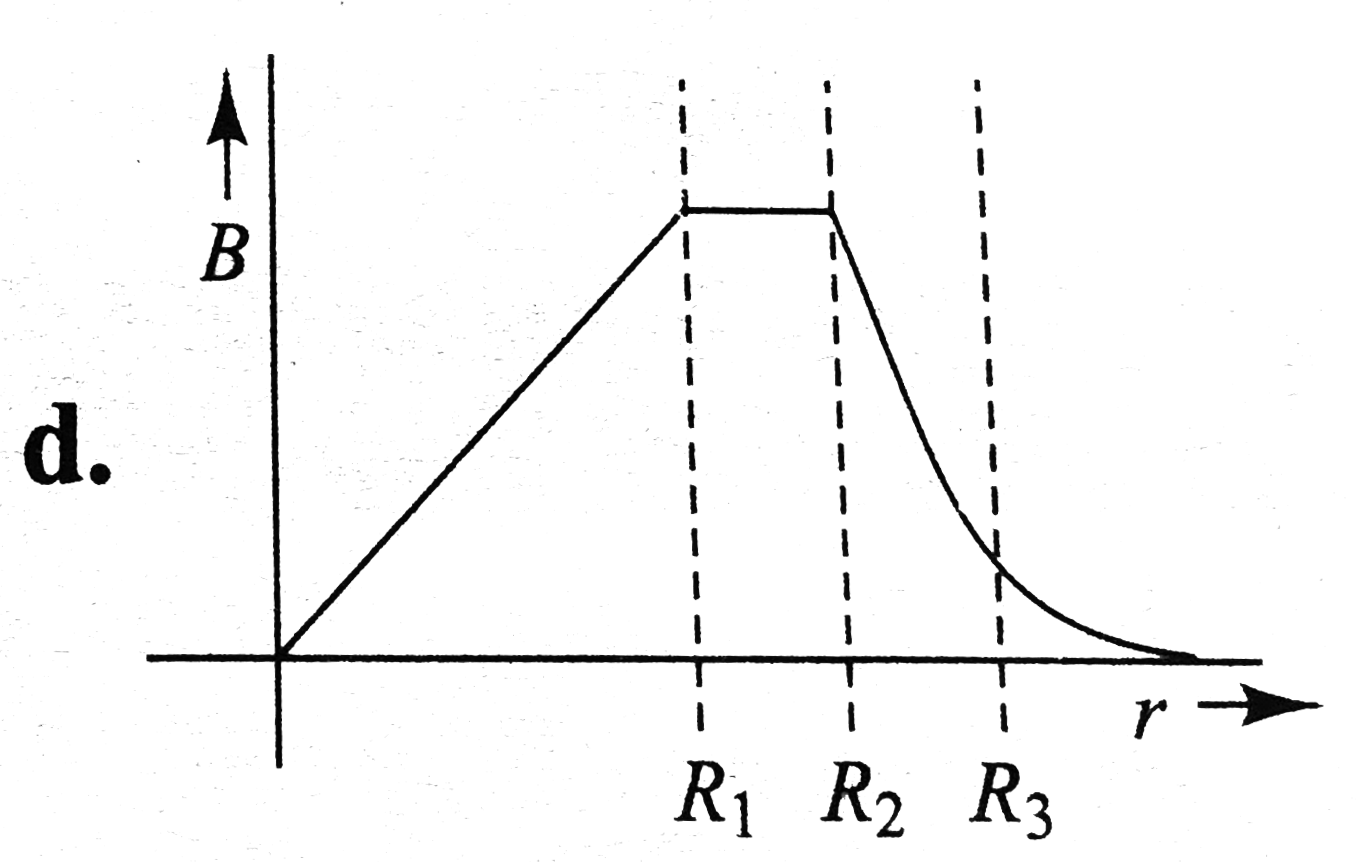A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
SOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise (multiple Currect )|5 VideosSOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise (assertion-reasioning )|2 VideosSOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise (subjective )|10 VideosRAY OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise DPP 1.6|12 VideosWAVE OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehension Type|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-SOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD-Exercise (single Correct )
- Three infinite current carrying conductors are placed as shown in Fig....
Text Solution
|
- An equilateral triangular loop is kept near to a current carrying long...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving wirh velocity vecv=hati+3hatj and it produces an ...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel plate capacitor is moving with a velocity of 25 ms^-1 throu...
Text Solution
|
- Current I flows around the wire frame along the edge of a cube as show...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig ABCDEFA was a square loop of side l, but is folded in two equal...
Text Solution
|
- If the magnetic field at P can be written as K tan (alpha/2),
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic field at the origin due to the current flowing in the wir...
Text Solution
|
- Two infinitely long linear conductors are arranged perpendicular to ea...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows an Amperian path ABCDA. Part ABC is in vertical plane PST...
Text Solution
|
- A coaxial cable made up of two conductors. The inner conductor is soli...
Text Solution
|
- From a cylinder of radius R, a cylider of radius R//2 is removed, as s...
Text Solution
|
- Current I enters at A in a square loop of uniform resistance and leave...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length l is used to form a coil. The magnetic field at its c...
Text Solution
|
- The value of the electric field strength in vacuum if the energy densi...
Text Solution
|
- Figure. Shows a small loop carrying a current I. The curved portion is...
Text Solution
|
- Three rings, each having equal radius R, are placed mutually perpendic...
Text Solution
|
- Positive point charge q=+8.00muC and q'=+3.00muC are moving relative t...
Text Solution
|
- Four very long, current carrying wires in the same plane intersect to ...
Text Solution
|
- Two very long, straight wires carrying, currents as shown in Fig. Find...
Text Solution
|