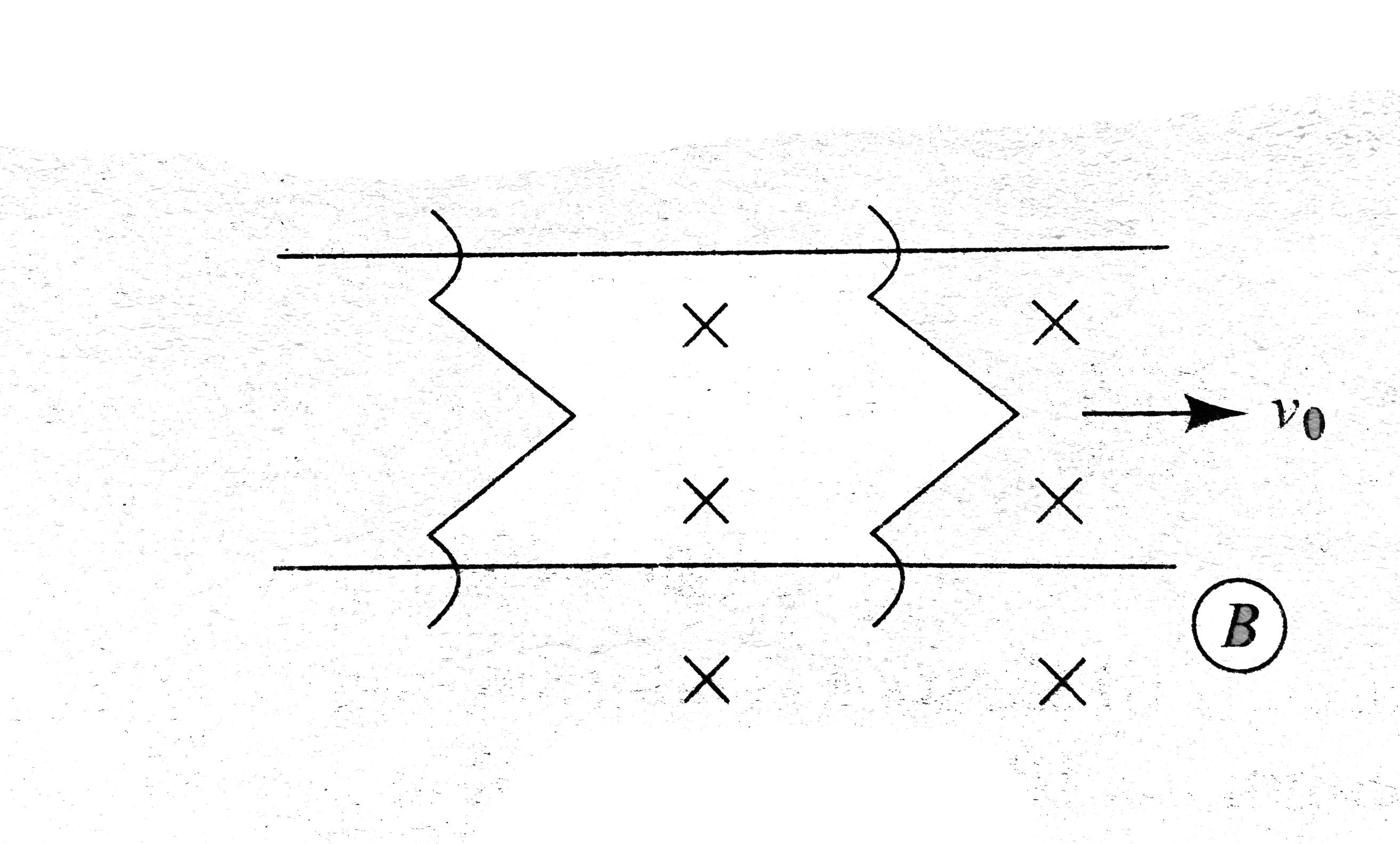
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Fill In The Blanks|3 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Single Correct|11 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Linked Comprehension|36 VideosELECTRICAL MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise M.C.Q|2 VideosELECTRON,PHONTS,PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT & X-RAYS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 3.3|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-Exercises Integer
- In Fig. ABCD is a fixed smooth conducting frame in horizontal plane. T...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a conducting rod of length l = 10 cm, resistance R and ma...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic field of a cyclindrical magnet that has a pole face radiu...
Text Solution
|
- a long coaxial cable consits of two thin-walled conducting cyclider ca...
Text Solution
|
- A circular coil of wire consists of exactly 100 turns with a total res...
Text Solution
|
- Some magnetic flux is changed from a coil of resistance 10Omega. As a ...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. there are two sliders and they can slide on two frictionless ...
Text Solution
|
- A square wire loop of 10.0 cm side lies at right angles to a uniform m...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform magnetic field B = 0.5 T exists in a circular region of radi...
Text Solution
|